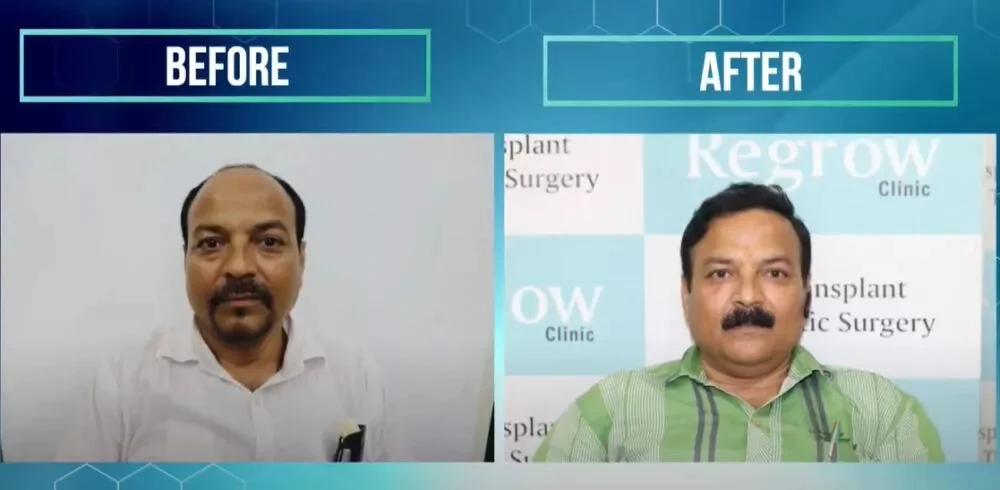
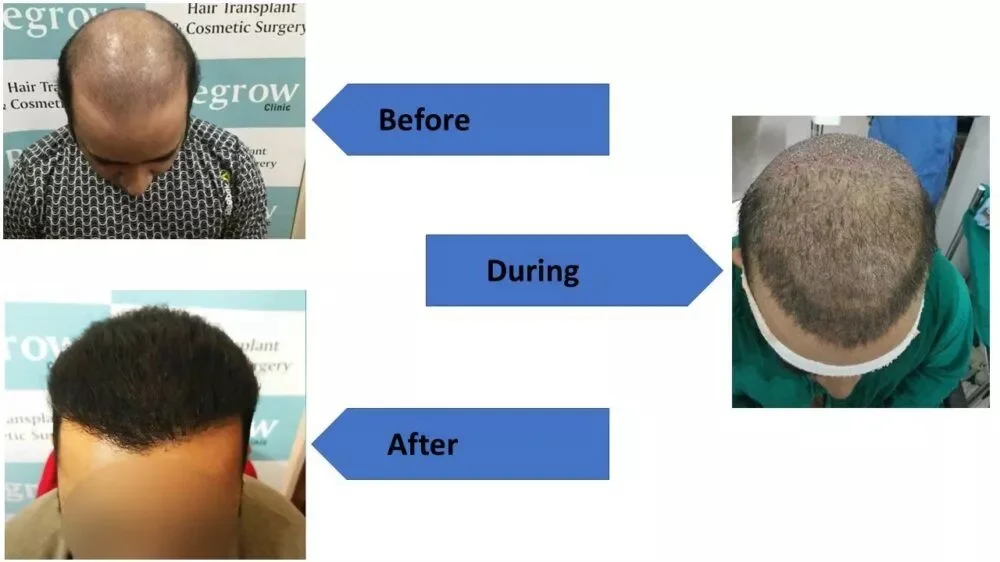
Male Pattern Baldness: What You Need to Know

Introduction: When Hair Starts to Fade
Have you ever glanced in the mirror and noticed your hairline creeping back? Or found more strands on your pillow than usual? If so, you’re far from alone. Male pattern baldness (MPB) is a reality for millions of men worldwide — and it’s much more than a simple cosmetic concern. It touches confidence, identity, and even social interactions. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about male pattern baldness — from its causes and stages to the most effective treatments, including hair transplant options offered at QHT Clinic. Whether you’re just starting to notice thinning or already considering a hair transplant, this guide will help you understand your options clearly and scientifically, with language that’s both relatable and precise.
What Is Male Pattern Baldness?
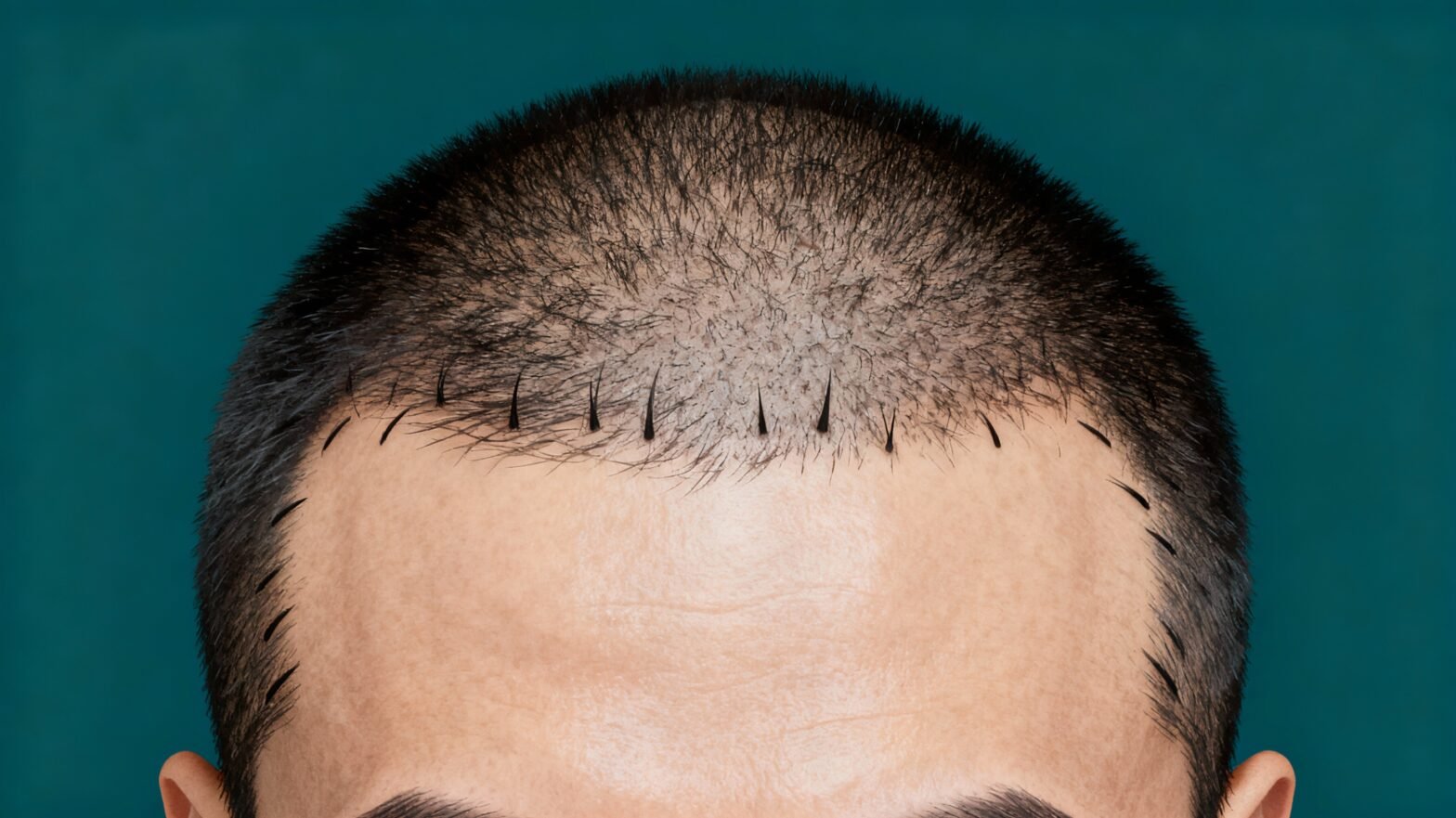
Male pattern baldness, medically called androgenetic alopecia, is the most common type of hair loss in men. It’s characterised by a predictable pattern, usually starting with thinning at the temples and crown. Over time, these areas expand, sometimes leaving only a rim of hair around the sides and back of the head. The science behind this condition involves a hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT) — a derivative of testosterone. In men genetically predisposed to MPB, DHT binds to receptors in hair follicles, causing them to shrink. This process, called follicular miniaturisation, results in hair becoming thinner, shorter, and eventually ceasing growth altogether.Causes of Male Pattern Baldness: Genetics, Hormones, and More
You might wonder, “Why am I losing hair?” The causes of male pattern baldness are complex but mainly boil down to genetics and hormonal factors:1. Genetics
Genetics plays a crucial role. If your father, grandfather, or close male relatives experienced hair loss, there’s a high chance you might too. Studies have identified several genes involved, including those related to androgen receptors, which influence how your scalp reacts to DHT.2. Hormones
DHT, a potent androgen hormone, is the main culprit. It’s produced when testosterone is converted by the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. Hair follicles sensitive to DHT gradually shrink, reducing the hair growth phase and producing thinner hairs until the follicles stop producing hair.3. Ageing
As you get older, hair naturally thins. The growth cycle shortens, and follicles produce finer hair. Ageing compounds the effects of DHT, accelerating hair loss4. Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Though not primary causes, factors like chronic stress, poor diet, smoking, and certain medical conditions (e.g., thyroid disorders) can exacerbate hair loss or trigger temporary shedding.Male Pattern Baldness Stages: The Norwood Scale
 To classify and understand the progression of MPB, experts use the Norwood Scale, which categorises the extent and pattern of hair loss:
To classify and understand the progression of MPB, experts use the Norwood Scale, which categorises the extent and pattern of hair loss:
- Stage 1: No significant hair loss; the hairline remains intact.
- Stage 2: Minor recession around the temples.
- Stage 3: Deeper receding hairline forming an “M” shape; first signs of baldness.
- Stage 4: More pronounced hairline recession and thinning at the crown.
- Stage 5: Hair loss at the temples and crown enlarge but remain separated by a thin band.
- Stage 6: The band between the two balding areas disappears, creating a larger bald spot.
- Stage 7: The most severe stage, where only a band of hair remains around the sides of the scalp.
- Norwood Stage 1 – Minimal hair loss. No grafts usually needed.
- Norwood Stage 2 – Slight recession of the hairline. Grafts may be required for cosmetic improvement (500–800 grafts)
- Norwood Stage 3 – Deep recession at the temples and mild thinning at the crow(1000–1600 grafts).
- Norwood Stage 4 – Noticeable balding at both the crown and front areas (1600–2400 grafts).
- Norwood Stage 5 – Bridge between the crown and front starts thinning (2400–3200 grafts).
- Norwood Stage 6 – Extensive hair loss, crown and frontal hairline merge (3200–4000+ grafts).
- Norwood Stage 7 – Only a band of hair remains at the sides and back (4000–6000+ grafts if feasible).
Factors That Influence Graft Requirements
Now, the real question: Why can’t I just pick a stage and go with that number? Because hair restoration is a personalised journey, and these numbers are simply starting points. Your graft requirement depends on:- Scalp Laxity: Scalp flexibility impacts how easily grafts can be harvested and placed. A loose scalp often allows for more efficient extraction and implantation.
- Hair Density in Donor Area: This refers to the number of hair follicles per square centimetre in the back or sides of your scalp. Higher density = more grafts available.
- Hair Characteristics: Thick, curly, or wavy hair offers better coverage than fine, straight hair, meaning fewer grafts may be needed for the same visual effect.
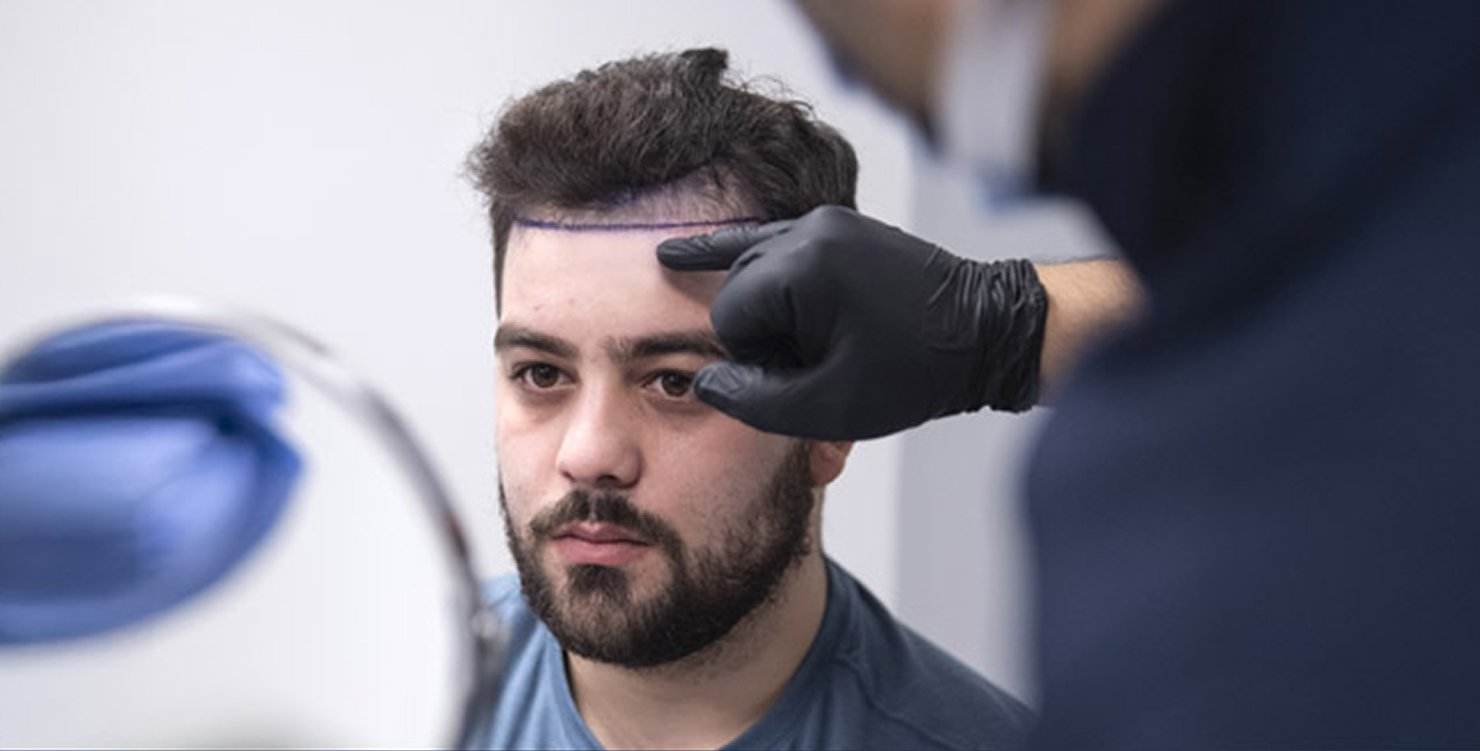
- Desired Hairline and Coverage: A lower or denser hairline will require more grafts.
- Age and Future Hair Loss: If you’re young and still experiencing progressive hair loss, a conservative grafting approach is often advised to reserve grafts for future use.
- Ethnic and Individual Differences: For example, people of African descent may have curlier hair that offers more coverage per graft, whereas people of East Asian descent may require more grafts for a similar effect.
Early Signs of Hair Loss: What to Watch For
Recognising the early indicators of male pattern baldness can significantly improve your chances of managing or slowing its progression. Here are some of the most common — and often overlooked — early warning signs:● Gradual Thinning or Receding Hairline:
One of the earliest signs is a subtle change in your hairline, often forming an “M” shape as the hair begins to recede at the temples. This change can be so gradual that it’s only noticeable by comparing old photographs or with the help of a mirror and good lighting.● Increased Hair Shedding:
Noticing more hair than usual on your pillow, in the shower drain, or on your hairbrush could indicate the start of hair loss. While some daily shedding is normal (around 50–100 strands), a noticeable increase might be a red flag.● Widening of the Parting Line:
If you part your hair, pay attention to whether the line is becoming broader over time. A widening part is a subtle sign that your hair density is decreasing, especially at the crown or frontal scalp.● Thinner or Weaker Hair Strands:
You may find that your hair doesn’t feel as thick or strong as it once did. This is often due to follicular miniaturisation, where each strand becomes finer with every growth cycle, eventually becoming barely visible.● Increased Visibility of the Scalp:
If your scalp is becoming more visible — particularly under bright light or in photos — it may be due to thinning hair. This is especially noticeable around the crown and hairline.● Changes in Hair Styling Difficulty:
If your usual hairstyle isn’t sitting right, or you find it harder to create volume or coverage, it could be due to an overall decrease in hair density. If you’re experiencing one or more of these signs, it’s important to consult a hair restoration expert. Early intervention can slow progression, maintain existing hair, and increase your chances of achieving successful results — whether through medical therapies, non-invasive treatments, or future transplant planning.Male Pattern Baldness Treatment Options: From Medication to Surgery
Fortunately, advances in science have provided various options to slow, halt, or even reverse hair loss. Let’s explore the most common treatments:1. Medical Treatments
Minoxidil: An FDA-approved topical treatment that promotes hair growth by increasing blood flow to follicles. It is available over the counter and can slow hair loss or help regrow hair if used consistently. Finasteride: An oral prescription medication that inhibits 5-alpha reductase, thereby reducing DHT levels. Clinical studies show that finasteride can slow hair loss and even regrow hair in many men. Note: Both medications require ongoing use to maintain results. Side effects may occur, so consult a healthcare professional before starting2. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy uses your own blood’s platelets to stimulate hair follicles. After blood is drawn and processed, the platelet-rich plasma is injected into the scalp, promoting natural growth factors. PRP is often used as a complementary treatment alongside other therapies.3. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT uses specific wavelengths of light to stimulate hair follicles, enhancing cellular activity and circulation. It’s a non-invasive option sometimes combined with medical treatments.4. Hair Transplant Surgery
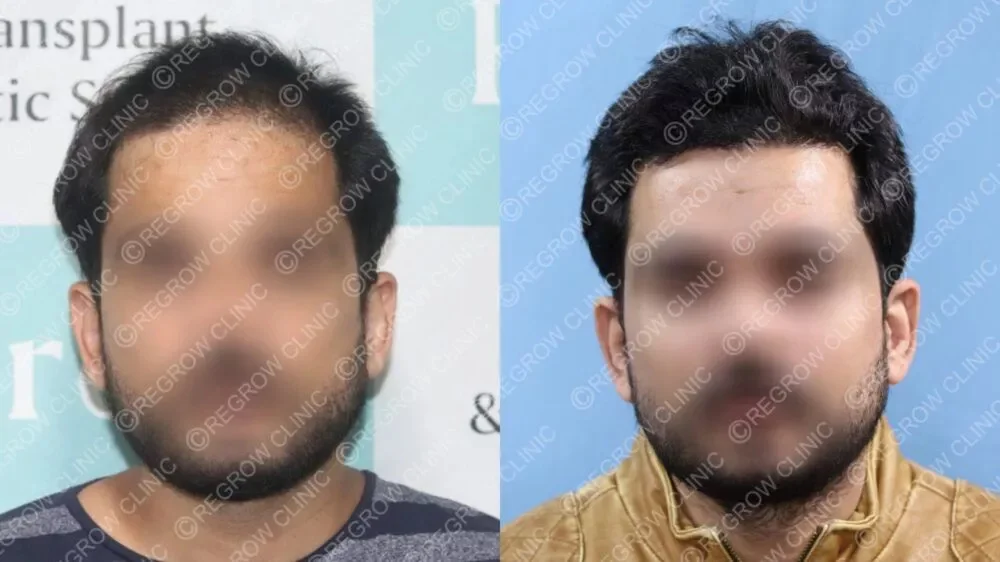
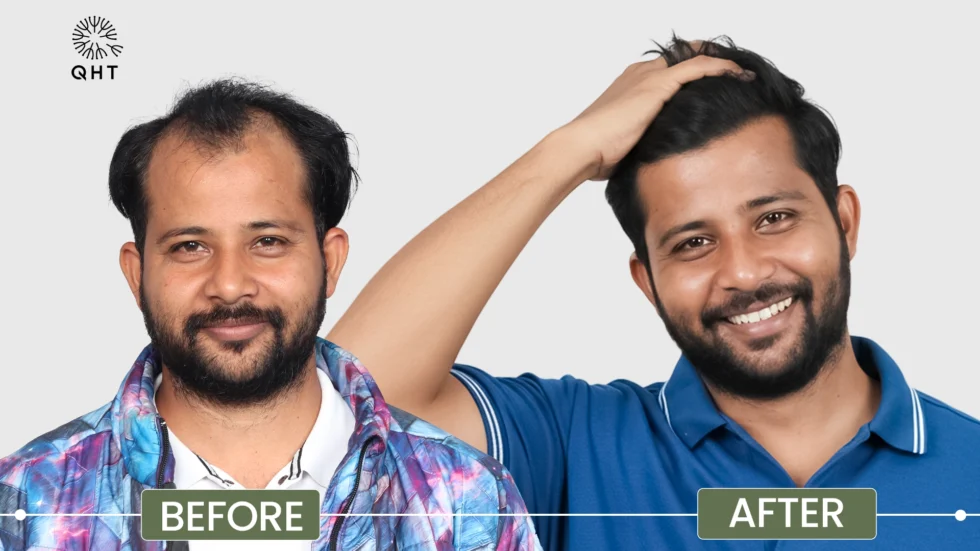
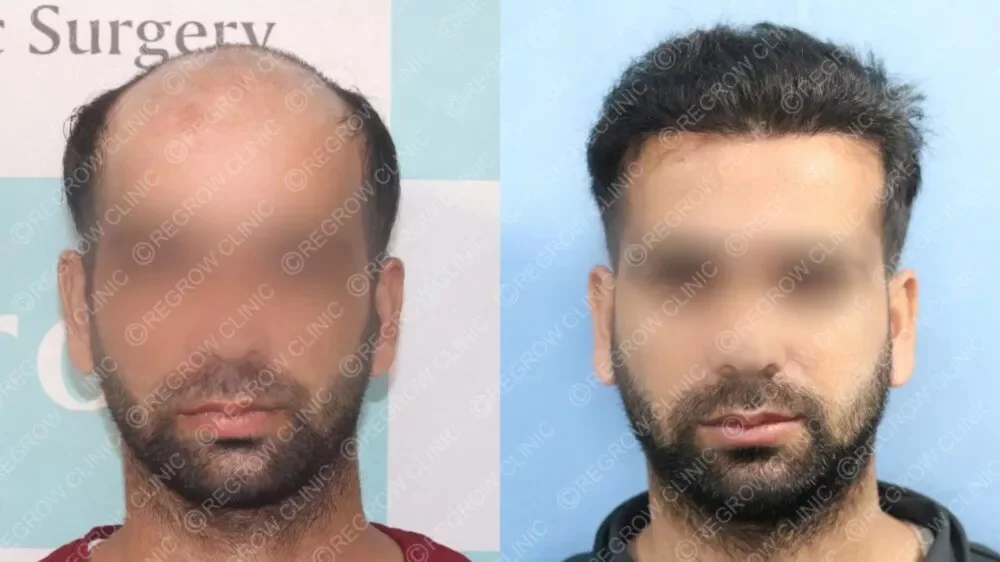
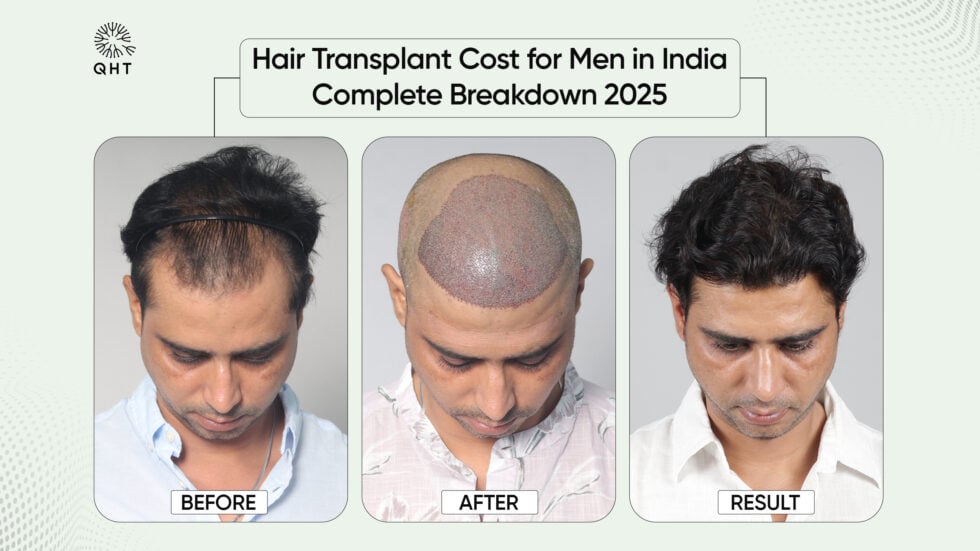
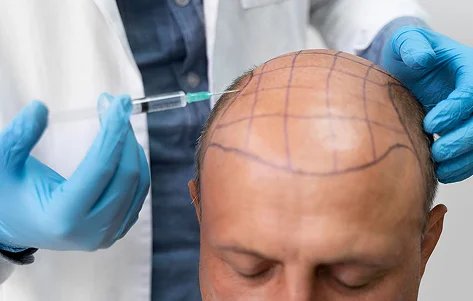
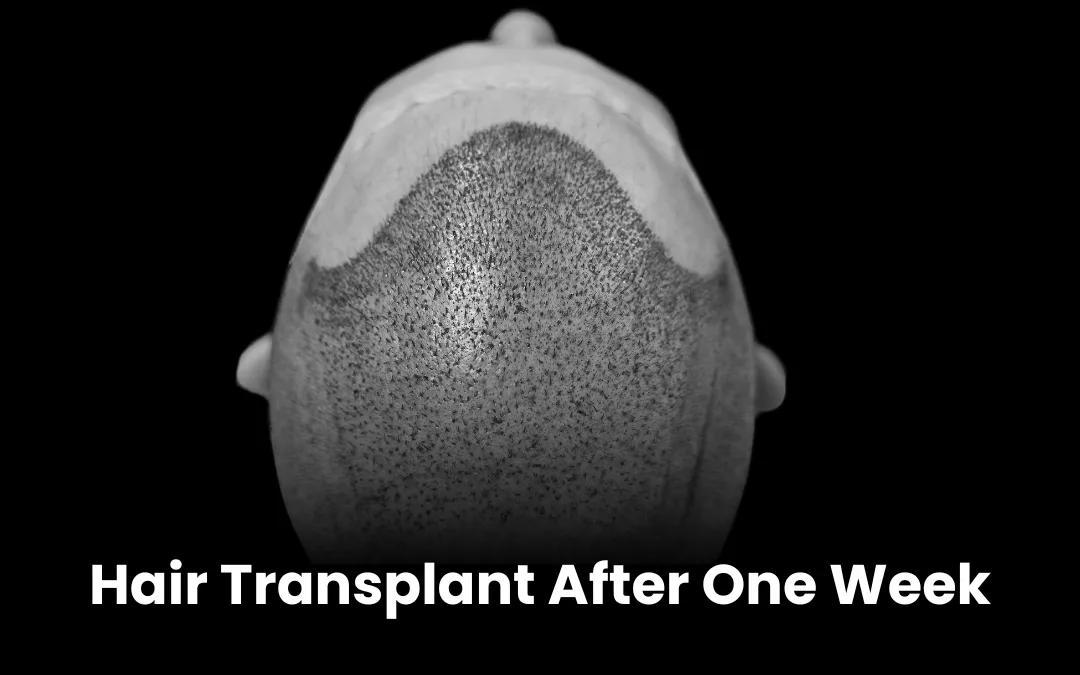
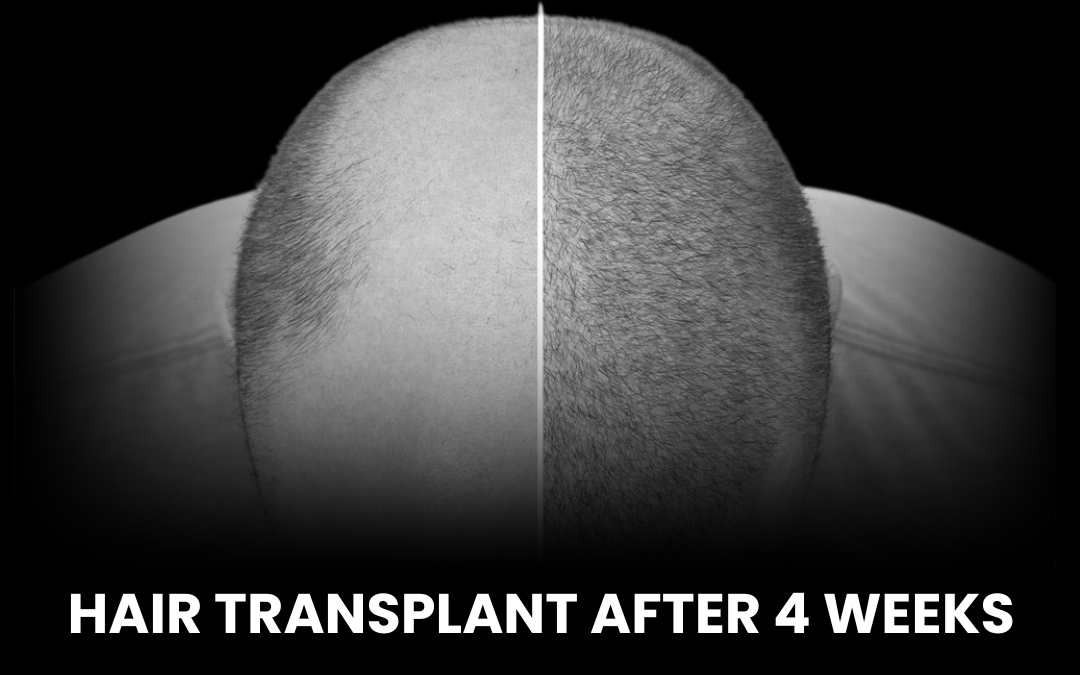
Hair transplant is considered the gold standard for permanent hair restoration, especially in advanced stages of male pattern baldness. Two primary techniques are:- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): Individual follicular units are harvested directly from the donor area and transplanted to thinning regions. This method leaves minimal scarring and has a quicker recovery.
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): A strip of scalp is removed from the donor area, and individual follicular units are dissected and transplanted. This allows for more grafts in a single session but leaves a linear scar.
Why Choose Hair Transplant at QHT Clinic?
When considering a hair transplant, the clinic you choose can make all the difference — not just in results, but in the entire experience. At QHT Clinic, we don’t believe in one-size-fits-all solutions. Our approach is highly personalised, scientifically grounded, and designed to give you natural-looking, long-lasting results that complement your unique features.- Personalised Hairline Design with Precision Mapping: Every face is different — and so is every hairline. At QHT Clinic, we use high-definition digital scalp mapping to assess the current state of your scalp and hair. This enables us to design a customised hairline that suits your facial structure, age, and the specific stage of hair loss (Norwood classification). The goal is to restore not just hair, but your original expression and appearance — subtly, artfully, and authentically.
- A Team That Prioritises Quality Over Quantity: Our team of highly trained experts focuses on two critical aspects that define a successful hair transplant: follicular survival rate and natural hair direction. Precision placement ensures that each graft aligns with your native growth pattern, resulting in a finish that is nearly indistinguishable from your natural hair.
- Advanced Techniques for Higher Graft Yield and Faster Recovery: We employ cutting-edge techniques such as minimally invasive extraction methods and refined implantation tools that cause less trauma to the scalp. This not only increases the survival rate of each graft but also promotes faster healing. Most patients can resume daily activities shortly after the procedure, with noticeable improvements in density and texture in the months that follow
- Support That Goes Beyond Surgery: A transplant is not the end of your hair journey— it’s the beginning of a new chapter. At QHT Clinic, we provide ongoing post-operative care and guidance to help maintain the health of both your transplanted and native hair. From follow-up check-ins to expert advice on hair nutrition and care routines, our support system is designed to maximise your results and confidence.
Common Myths and Facts About Male Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness is one of the most common causes of hair loss in men — yet, despite how widespread it is, myths and misinformation still surround it. Separating fact from fiction is essential if you’re considering treatment or simply trying to understand your own hair loss better. Let’s debunk some of the most common myths:Myth 1: Wearing Hats Causes Baldness
Fact: Hats don’t cause hair loss; genetics and hormones do. One of the oldest and most persistent myths is that frequent hat-wearing suffocates your scalp and causes your hair to fall out. In reality, hair follicles receive oxygen and nutrients through the bloodstream, not from the air. Unless the hat is excessively tight and constantly causing friction or pulling hair (a rare scenario), it has no role in triggering male pattern baldness. The real culprits are androgens, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT), and your genetic predisposition.Myth 2: Hair Loss Only Affects Older Men
Fact: Male pattern baldness can begin in your late teens or early 20s. Although hair thinning is more visible with age, male pattern baldness can start surprisingly early. Many men begin to notice receding hairlines or thinning at the crown in their 20s or even late teens. Early onset doesn’t mean it’s abnormal — it just reflects how strongly your genes and hormonal responses are wired. The sooner you identify the signs, the more proactive you can be with treatments and lifestyle adjustments.Myth 3: Frequent Shampooing Causes Hair Loss
Fact: Washing your hair doesn’t cause it to fall out — in fact, it can help maintain scalp health. It’s common to notice loose hairs while shampooing, leading many to believe that washing is causing hair loss. The truth is, those hairs were already in the shedding (telogen) phase of the hair cycle and would have fallen out anyway. Shampooing helps cleanse the scalp, reduce build-up, and support a healthy environment for hair growth. The key is to choose a gentle shampoo suitable for your hair type and avoid excessive scrubbing or harsh chemicals.Myth 4: Hair Loss Comes Only from Your Mother’s Side
Fact: Genetics from both sides of the family play a role. While it’s true that the AR gene on the X chromosome (inherited from your mother) influences androgen receptors, hair loss is a polygenic condition, meaning multiple genes from both parents contribute. So if your father or maternal grandfather had significant hair loss, your risk might be higher — but it’s not limited to your mum’s side of the family.Myth 5: Stress Is the Main Cause of Male Pattern Baldness
Fact: Stress can contribute to temporary shedding, but male pattern baldness is largely hormonal and genetic. Severe stress can trigger a condition called telogen effluvium, where a large number of hairfollicles enter the resting phase prematurely. However, this type of hair loss is typically temporary. Male pattern baldness, on the other hand, is a chronic and progressive condition driven by sensitivity to DHT. That said, managing stress can still be beneficial for your overall hair and scalp health. Understanding the facts allows you to approach your hair loss journey with confidence, realistic expectations, and clarity. Misinformation not only causes unnecessary worry but can also delay appropriate treatment. If you’re unsure about what’s causing your hair loss or what steps to take next, speaking with a hair restoration expert — like those at QHT Clinic — can provide clear, science-backed answers.Can Male Pattern Baldness Be Prevented?
While you cannot change your genetic makeup, lifestyle choices can slow hair loss progression:- Balanced nutrition rich in vitamins (especially B-complex, D, E, iron, zinc).
- Stress management through exercise or mindfulness.
- Avoiding harsh hair treatments and heat styling.
- Early consultation with a hair specialist when thinning begins.
Emotional and Social Impact of Hair Loss
Hair plays a powerful role in identity and self-esteem. Losing it can cause distress, anxiety, or even depression. Remember, hair loss does not define your worth or masculinity. Seeking treatment is a step towards reclaiming confidence. Support groups, counselling, or speaking with professionals can also help manage the emotional toll.Realistic Expectations: What a Hair Transplant Can and Cannot Do
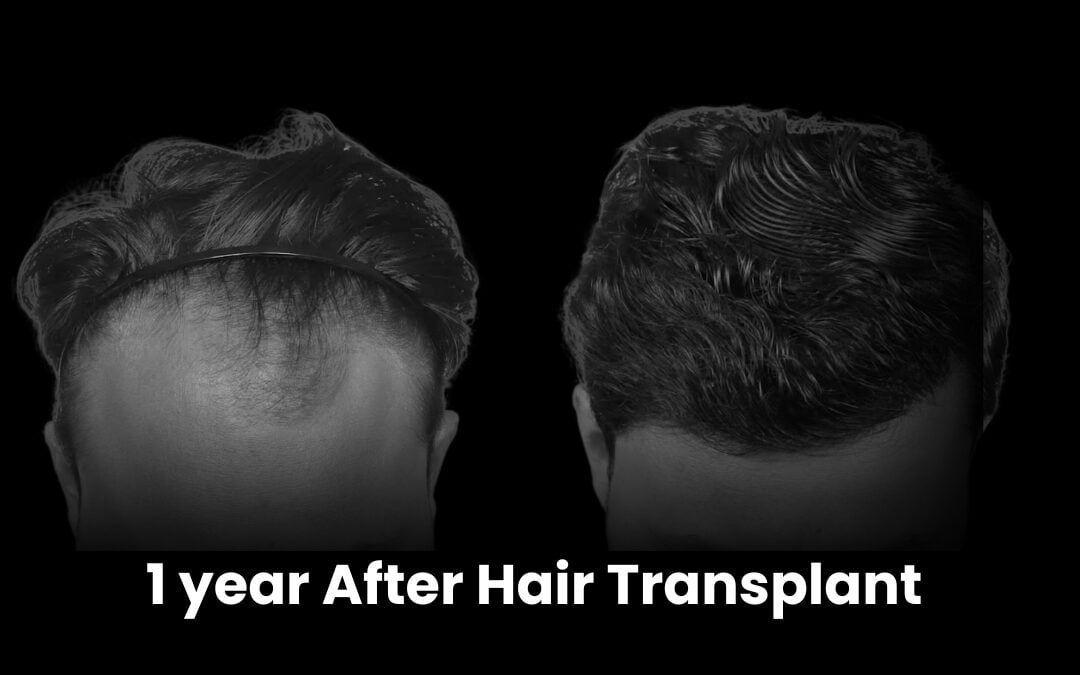
Hair transplant is effective but has limits:- Results take time: New hair typically grows within 3–4 months, with full results at 9–12 months.
- Maintenance: Some ongoing treatments may be needed to preserve existing hair.
- Suitability: Diffuse hair loss or very advanced cases may require alternative strategies.
Let’s Answer Some Real Questions
Is hair transplant painful?
Minimal discomfort with local anaesthesia; most patients report manageable pain.Are results permanent?
Transplanted hair is permanent, but ongoing care is essential for native hair.How long is recovery?
Most resume normal activities within a week; full scalp healing takes several weeks.Will the hair look natural?
Yes. Natural hairline design and follicle placement ensure seamless appearance.Conclusion: Take Charge of Your Hair and Confidence
Male pattern baldness is a common but manageable condition. Whether at the first sign of thinning or advanced loss, understanding your condition and available treatments is empowering. At QHT Clinic, we combine cutting-edge science with personalised care to help you regain not just your hair but your confidence and self-esteem. Don’t let hair loss define you. Reach out to QHT Clinic for a detailed consultation and explore your options for a natural, lasting solution.Book a Consultation Today
Latest Videos
-

Rajpal Yadav | Bollywood Actor Hair Transplant Journey at QHT Regrow Clinic Haridwar
Click to Watch
-

FUE Hair Transplant Results | DAYA's FUE Hair Transplant Results
Click to Watch
-

Best Hair Transplant Result 2021 || NW Grade VI A || 3,422 Grafts
Click to Watch
-

Best Hair Transplant Result 2022 | Grade 4
Click to Watch
-

YouTuber Mehtab Saifi Hair Transplant
Click to Watch
-

ACP Pradyuman Hair Transplant - Actor's Hair Transplant
Click to Watch