Is Alopecia Areata Contagious?

Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly targets hair follicles, causing patchy hair loss. It can occur at any age and affects both men and women. This condition can be quite concerning for those affected, especially when they notice bald patches on their scalp or other body parts.
One common question patients often ask is, “Is alopecia areata contagious?” The answer is no; alopecia areata is non-contagious. However, the underlying causes, symptoms, and treatment options must be understood for effective management.
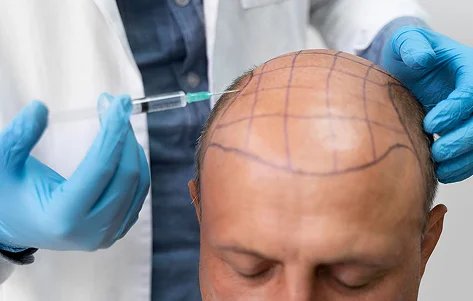
At QHT Hair Transplant Clinic in India, a team of experienced professionals specializes in treating various hair loss disorders, including alopecia areata. Depending on the severity, the experts offer effective medical and advanced hair restoration treatments such as FUE hair transplant for alopecia areata patients. With years of experience in managing alopecia-related conditions, the team is dedicated to helping patients regain their confidence through result-oriented treatments.
Worried about your hair loss condition? Get in touch with an expert for the right advice. Book your consultation today.
Wondering how alopecia areata affects hair loss? Let’s dive deeper into what this condition is all about.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks healthy hair follicles, leading to hair loss in round, smooth patches. This disorder can develop suddenly or over time and range in severity from minor patches to complete baldness. It often affects the scalp, but it can also impact eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair in severe cases.
Although not life-threatening, alopecia areata can significantly impact a person’s emotional well-being
due to the changes in appearance it causes. In most cases, alopecia areata does not cause permanent hair loss. Hair can regrow over time, but hair loss and regrowth cycles are common.
Wondering what triggers alopecia areata? Let’s dive into the root cause.
Is hair loss a symptom of diabetes?
due to the changes in appearance it causes. In most cases, alopecia areata does not cause permanent hair loss. Hair can regrow over time, but hair loss and regrowth cycles are common.
Main Causes of Alopecia Areata
Autoimmune Response: The immune system mistakenly targets hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
Key Features
Genetics: A family history of autoimmune diseases can increase the likelihood of developing alopecia areata.
Symptoms of Alopecia Areata
Environmental Factors: Stress, viral infections, or environmental triggers may initiate or worsen the condition.
Treatment for Alopecia Areata
Unknown Triggers: The exact cause remains unclear, and research is ongoing to understand all contributing factors.
Book Your Consultation Today
Take control of your hair health. Consult a specialist for expert guidance and care. Book your appointment now!
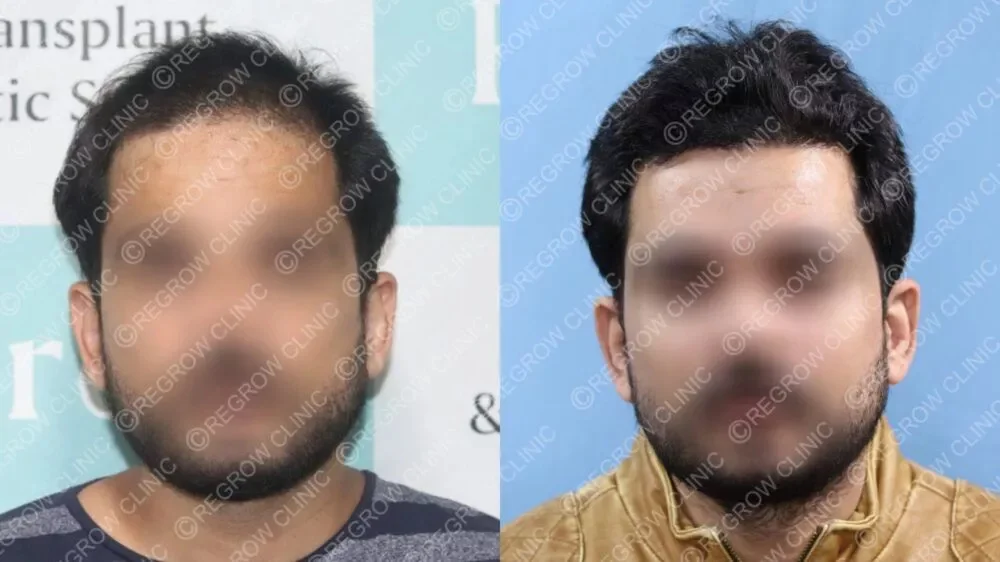
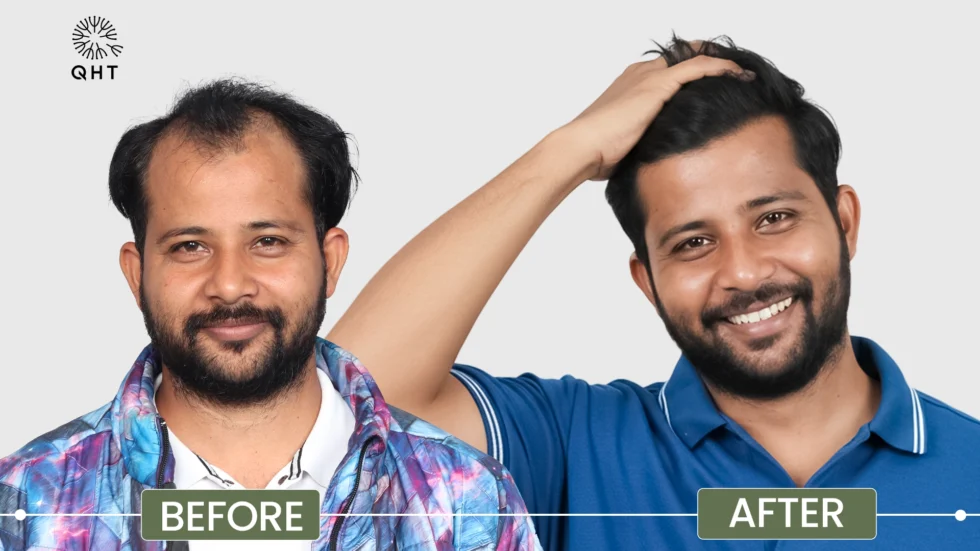
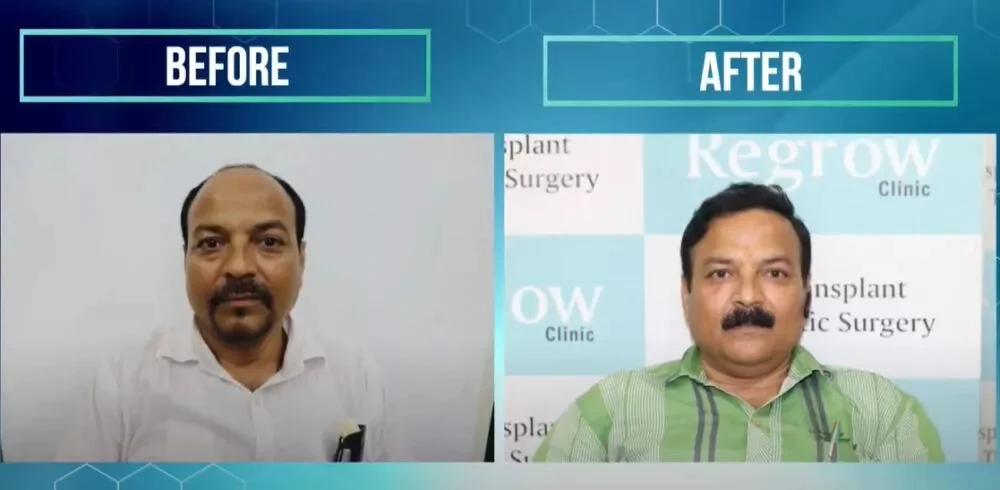
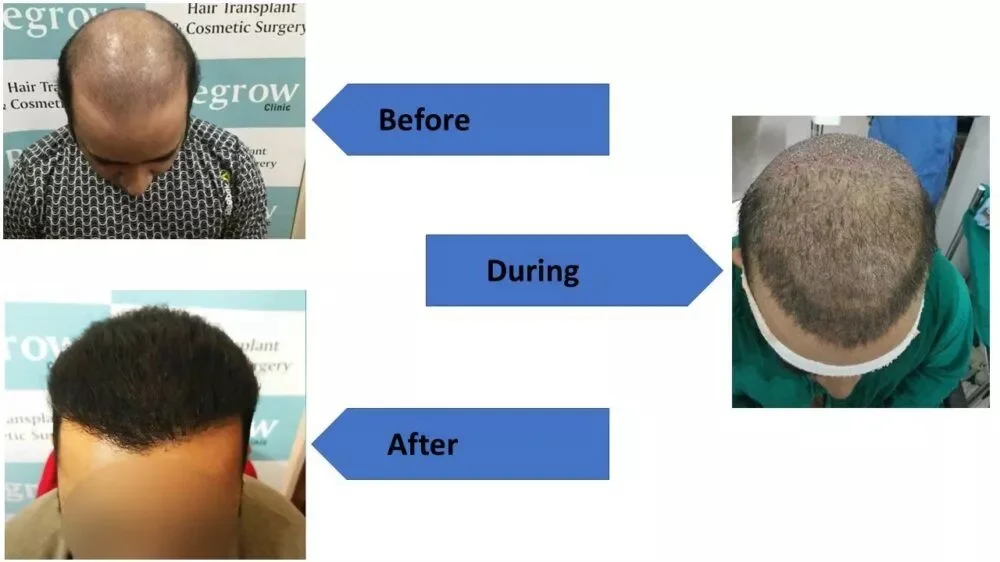
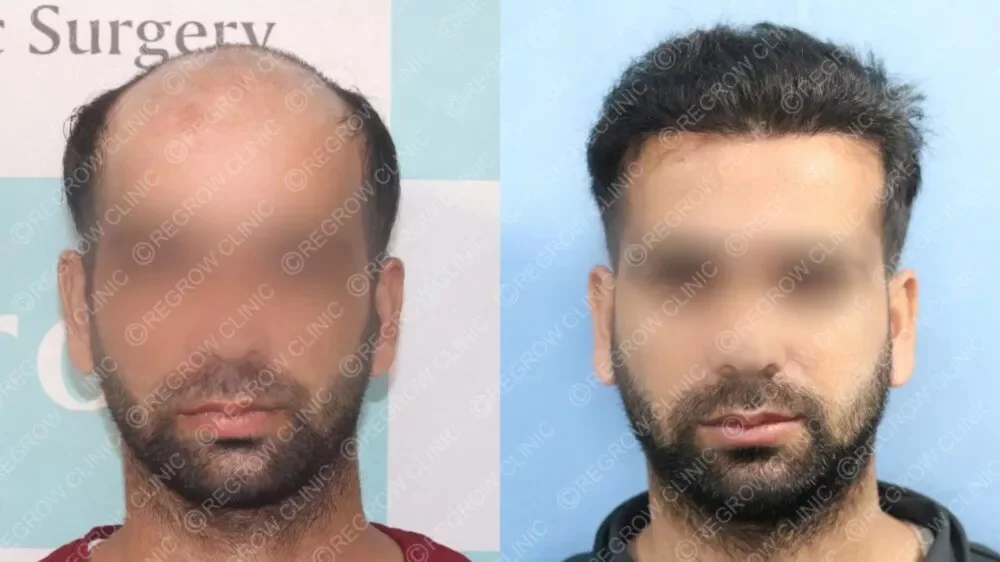
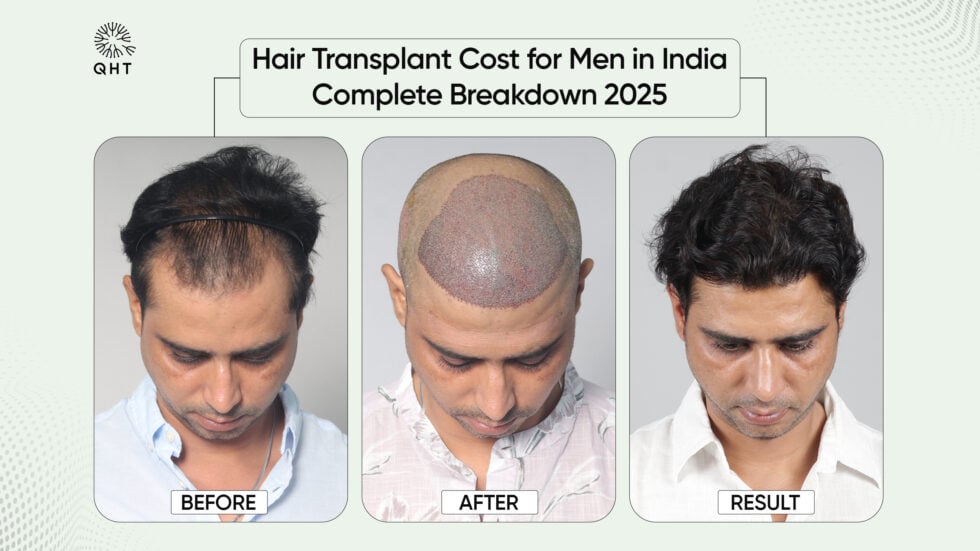
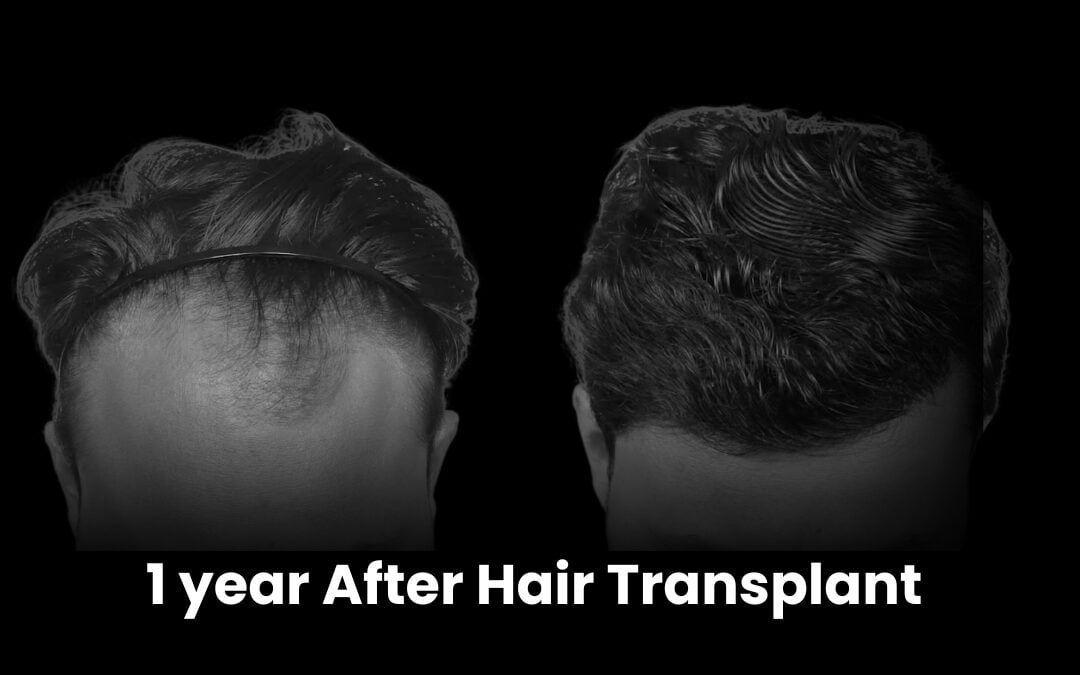
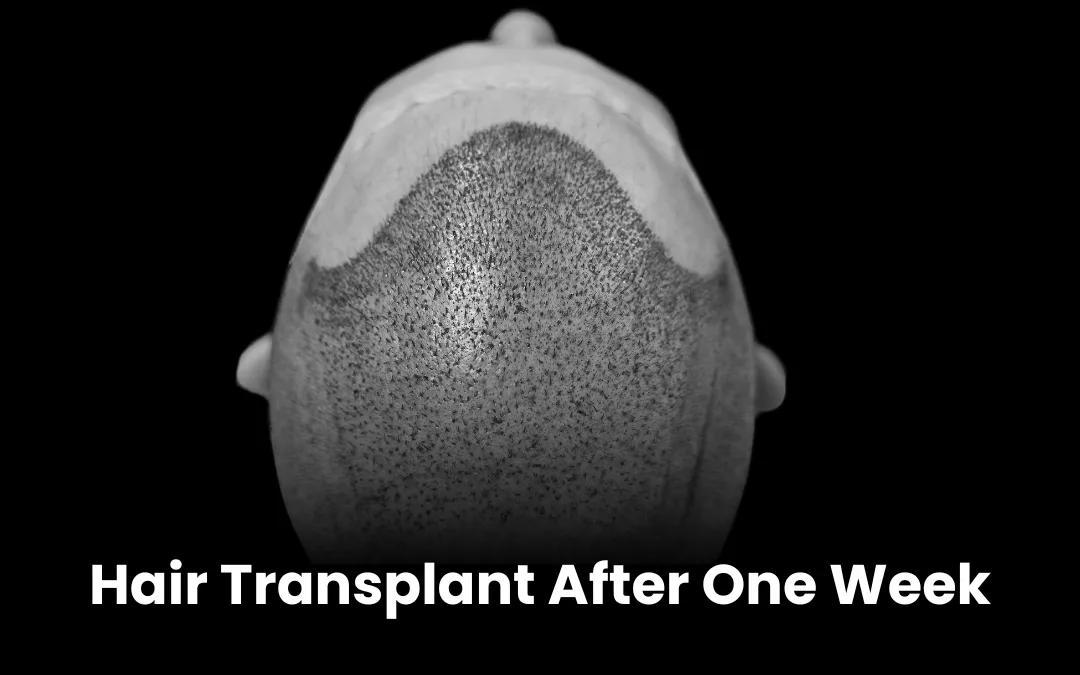
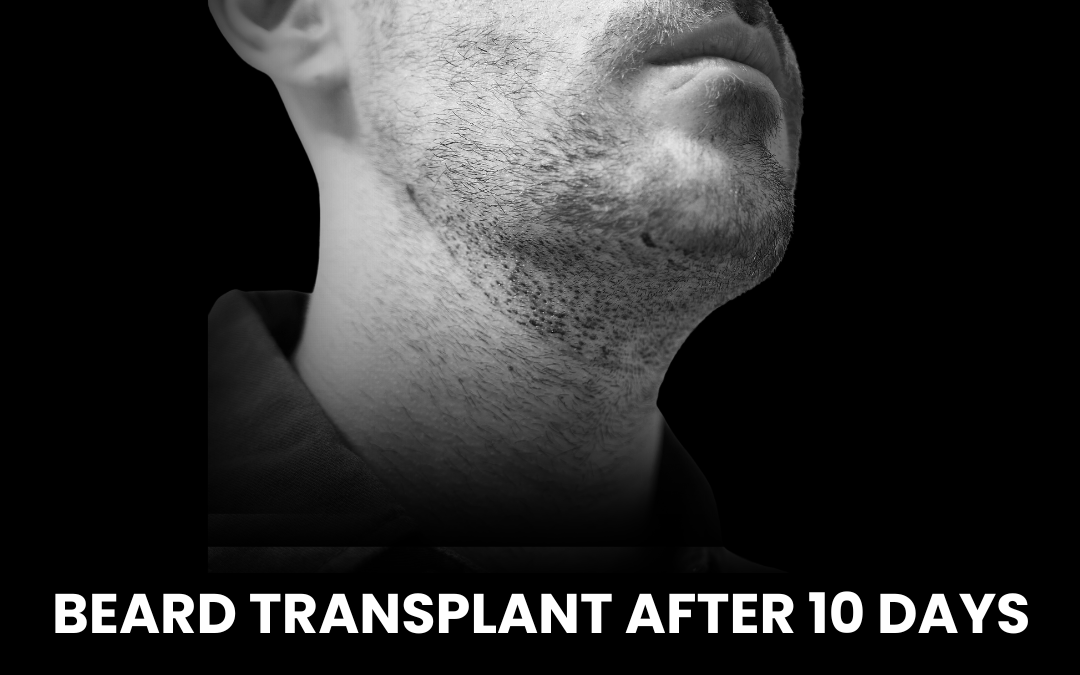
Our Successful Hair Transplant Results
Curious if alopecia areata can spread from one person to another? Let’s explore the facts.
Is Alopecia Areata Contagious?
Since alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition, there is no infectious agent involved that could spread it to others. Unlike conditions caused by bacteria or viruses, alopecia areata stem from a malfunction within the immune system, attacking the hair follicles. It’s an internal condition that cannot be passed from one person to another.
There is no risk of spreading alopecia areata through contact, shared items, or proximity to an affected individual.
How to Treat Alopecia Areata
It’s important to dispel any fears or myths about contagion, as this can lead to unnecessary social stigma for those struggling with the condition.
Preventing Alopecia Areata
Noticing unusual hair loss or bald spots? Let’s explore the symptoms next.
What Are the Symptoms of Alopecia?
The symptoms of alopecia can vary among individuals. However, the most common signs include:
Early Signs of Alopecia Areata
Sudden Hair Loss:
Hair often falls out in small, smooth, round patches on the scalp. It can also affect other areas, such as the beard, eyebrows, or eyelashes.
Nail Changes
Some people with alopecia areata notice small dents, white spots, or ridges forming on their fingernails or toenails.
Thinning or Weakening Hair:
Sometimes, hair may become thinner or weaker before falling out, particularly in the condition’s early stages. Tingling, Itching, or Burning Sensation:
Some individuals may experience a tingling or itching sensation on the scalp or the affected area before the hair loss occurs.
Changes in Nails:
Nail abnormalities such as pitting, ridging, or rough texture may accompany alopecia areata, which affects both hair and nails.
Hair Loss in Other Parts of the Body:
In more severe forms of Alopecia, such as Alopecia Totalis or Alopecia Universalis, there may be complete hair loss on the scalp or across the entire body.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s best to consult a medical professional for a diagnosis and to explore treatment options.
Understanding Alopecia Areata
Now, let’s explore the different types of alopecia.
Types of Alopecia
Alopecia can appear in several forms, each affecting hair growth differently. Understanding the types helps identify the right treatment approach and manage expectations for recovery.
Alopecia presents in various forms, ranging in severity and affected areas of hair loss:
Alopecia Areata (Patchy):
This is the most common type, where small, round patches of hair loss occur on the scalp or other body areas. The size and number of patches may vary, but they usually develop suddenly.
Alopecia Totalis:
This type involves complete hair loss on the scalp. It is a more advanced form of alopecia and can occur rapidly or over time.
Alopecia Universalis:
This is the most severe and rare form, where hair loss extends beyond the scalp to the entire body, including eyebrows, eyelashes, and even body hair. It can significantly impact daily life. Diffuse Alopecia Areata:
Unlike patchy hair loss, diffuse alopecia areata causes hair thinning across the scalp, resembling other conditions like telogen effluvium. It may be mistaken for regular hair thinning but is caused by an autoimmune reaction.
Ophiasis Alopecia:
This type affects the hairline and causes hair loss in a band-like pattern around the sides and back of the scalp. Because of its unique location, it can be more challenging to treat.
Androgenetic Alopecia:
Often referred to as male or female pattern baldness, this type is related to genetics and hormones and causes gradual thinning over time.
Traction Alopecia:
Hair loss caused by repeated stress or pulling on the hair, often due to tight hairstyles.
How do doctors diagnose alopecia areata? Let’s explore the diagnostic process.
How Is Alopecia Areata Diagnosed?
Alopecia areata is usually diagnosed through a physical examination of the hair loss pattern and scalp. In some cases, doctors may perform a scalp biopsy or blood test to rule out other autoimmune or hormonal conditions that could cause similar symptoms.
The symptoms of alopecia can vary among individuals. However, the most common signs include:
A dermatologist may gently pull a few hairs to check how easily they come out and examine the roots under a microscope to determine the extent of hair follicle damage.
Physical Examination: The doctor will first examine the affected areas to assess the extent and type of hair loss.
In some cases, a small scalp biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions that can cause similar patterns of hair loss.
Pull Test: This is a simple test in which the doctor gently pulls on hair to see how easily it comes out, which can help diagnose the severity.
Blood tests may be recommended to check for autoimmune disorders, thyroid problems, or nutritional deficiencies that might be contributing to hair loss.
Blood Tests: These are done to check for other autoimmune conditions that might be linked to Alopecia Areata.
In some cases, a scalp biopsy might be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other causes of hair loss.
Scalp Biopsy: In some cases, the doctor may remove a small sample of the scalp and send it for examination to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Alopecia Areata
Want a precise diagnosis for your hair loss? Consult a seasoned expert today for personalized care. Schedule an appointment now!
What Are the Treatment Options for Alopecia Areata?
What about treatment options for alopecia? Let’s explore the possibilities.
What Is the Treatment for Alopecia?
Treatment for alopecia areata focuses on stimulating hair growth and reducing inflammation around affected follicles. Depending on the severity, options may include topical or injected corticosteroids, immunotherapy, or advanced procedures such as PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy and hair transplantation.
Treating alopecia involves restoring hair growth and managing symptoms. Treatment choice depends on the severity and extent of hair loss. Some of the most effective treatment options include:
Topical corticosteroids or minoxidil may help stimulate regrowth in mild cases of alopecia areata.Hair Transplant for Alopecia Areata:
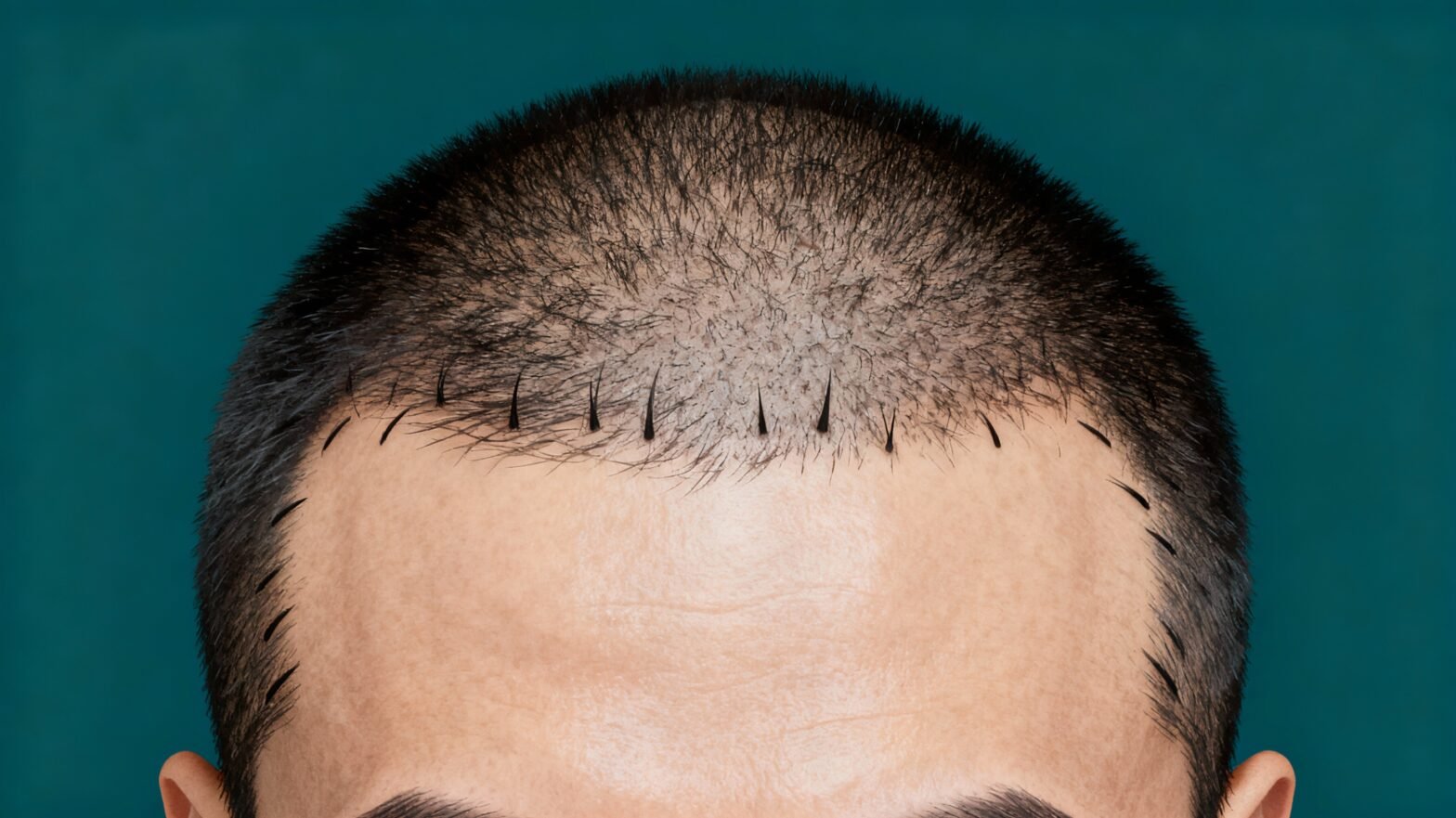
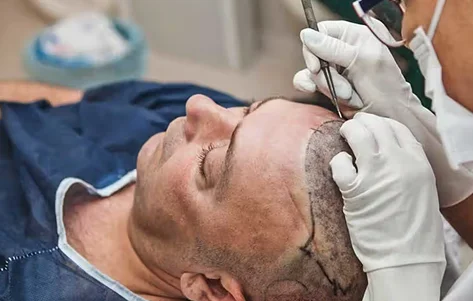
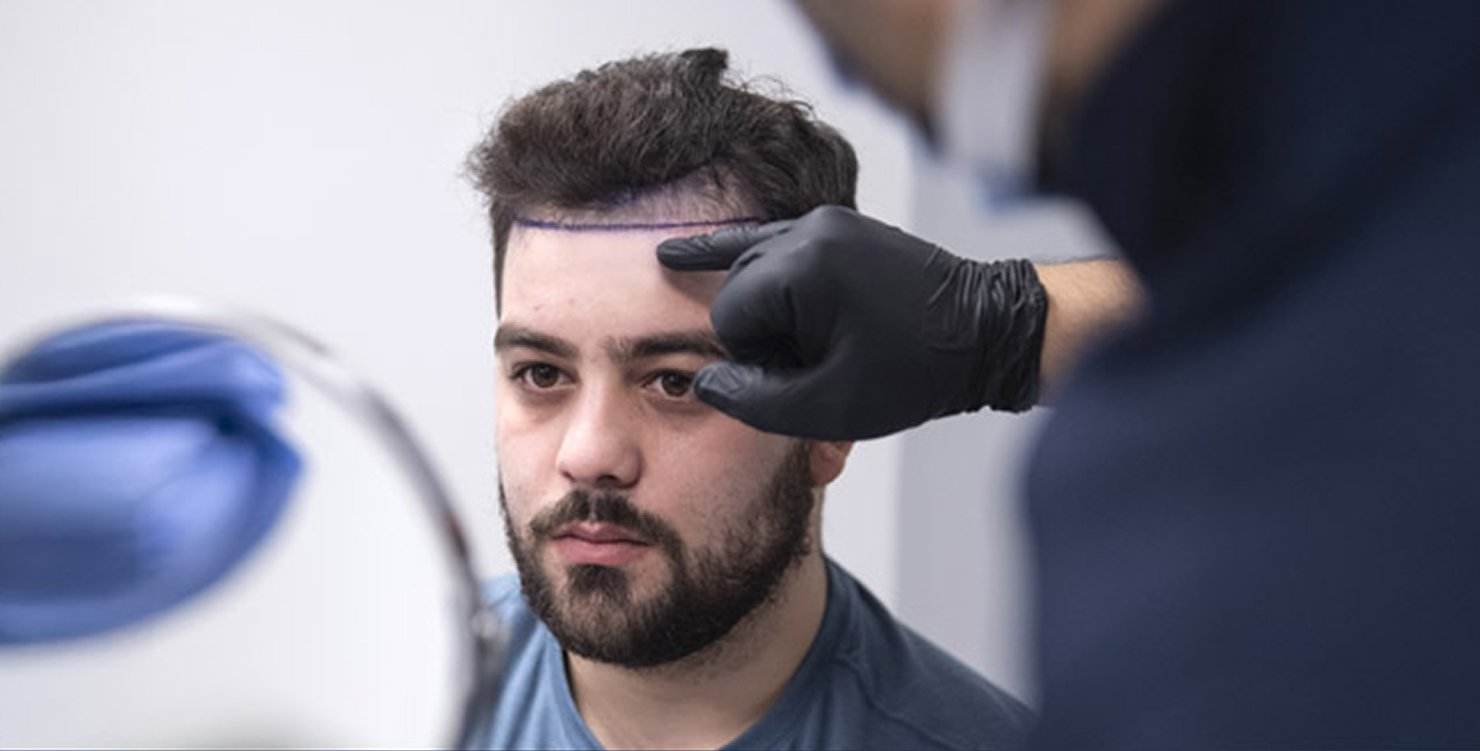
For people with alopecia areata, hair transplantation can be a viable option if the patient’s condition is stable and the hair loss is localized. The transplanted hair may grow and thrive as long as the underlying autoimmune condition is well-managed.
Experts often recommend Follicular Unit Extraction -FUE hair transplant for alopecia areata patients. It is a minimally invasive technique in which the surgeon extracts hair follicles from the donor site (back scalp or other body area) and implants them into the balding areas. This method is popular due to its quick recovery time and minimal scarring
- Use gentle hair care products to avoid further damage.
- Avoid excessive heat styling to protect hair follicles.
Topical Treatments:
Topical minoxidil can stimulate hair growth and is often used post-hair transplantation.
For more extensive hair loss, corticosteroid injections or oral immunosuppressants may be recommende
Corticosteroid Injections:
Injecting corticosteroids directly into the bald patches can help reduce inflammation and promote hair regrowth. This treatment may be used before or alongside hair transplant procedures.
Light therapy (phototherapy) may also be used to encourage hair regrowth in resistant cases.
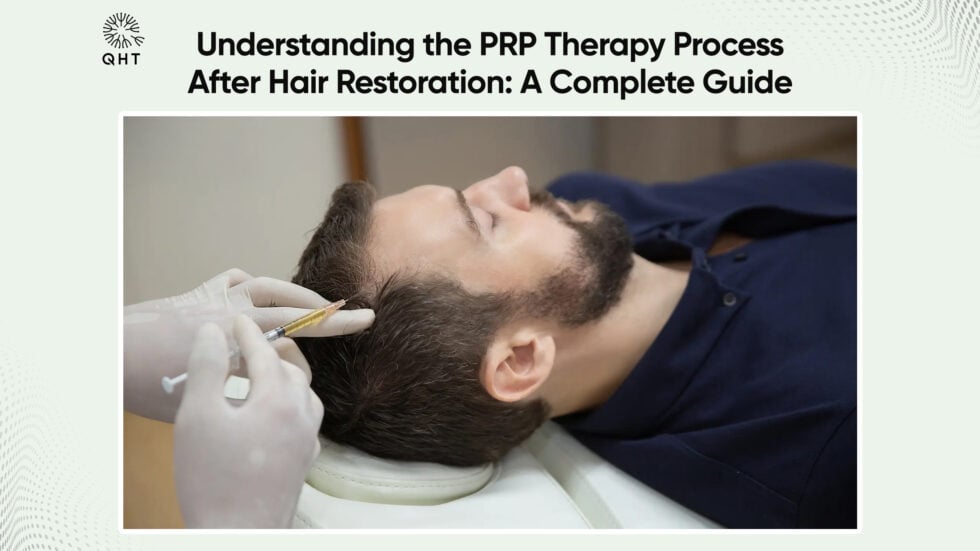
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
PRP therapy involves:
- Drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood.
- Processing it to concentrate the platelets.
- Injecting it into the scalp.
This may enhance hair follicle health and support hair transplant results.
In some cases, wearing wigs, scarves, or cosmetic camouflage can help improve appearance and confidence during treatment. Lifestyle and Supportive Treatments:
Incorporating a balanced diet, managing stress, and using gentle hair care products can improve overall hair health and complement medical treatments.Living with alopecia can be emotionally challenging, but various treatments and support options can help manage the condition effectively.
Can alopecia be prevented or managed? Let’s find out.
Maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support hair growth and scalp health.Healthy Diet:
To support hair health, consume a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly biotin, zinc, and iron.Regular scalp massages improve blood circulation, which can strengthen hair follicles and promote natural hair growth. Stress Management:
Practice stress-relief techniques such as Yoga, meditation, or regular exercise to reduce stress, which may trigger hair loss.Hair restoration treatments like PRP therapy and hair transplantation can offer long-term solutions for individuals experiencing significant hair loss. Gentle Hair Care:
Use mild shampoos and conditioners to avoid irritation. Avoid harsh treatments like colouring or chemical straightening.
Regular maintenance and follow-up sessions ensure long-lasting results and healthy hair growth.
Avoiding Tight Hairstyles:
Steer clear of hairstyles that pull on the hair, as tension can exacerbate hair loss.Our specialists use advanced techniques to ensure natural-looking and lasting results.Protective Measures:
Wear hats or scarves to shield the scalp from harsh weather conditions, such as extreme heat or cold.We provide personalized treatment plans to match your specific hair restoration needs.Regular Scalp Care:
Keep the scalp clean and well-moisturized to promote a healthy environment for hair growth.Experienced surgeons ensure minimal downtime and maximum comfort during every procedure. Follow-up with specialists:
Regularly consult a healthcare expert to monitor the condition and adjust treatment plans. Managing diabetes-related hair loss requires a balanced approach that includes proper blood sugar control, a nutritious diet, and the use of gentle hair care practices. Consulting a specialist can help determine the best treatment plan and improve overall hair health.
Alopecia areata may be challenging, but it’s non-contagious, and effective treatments are available. QHT Hair Transplant Clinic in India, known for its expertise in hair transplants for alopecia areata, offers a range of solutions tailored to your needs. Whether you’re considering a FUE hair transplant for alopecia or other hair restoration methods, QHT’s expert team is here to help you regain your confidence with the best hair grafting in India
Take control of your hair health today — book a consultation with our experts and discover personalized solutions for diabetes-related hair loss.
Consult with best hair surgeons in india for personalized solutions. Book an appointment now!
1. Can diabetes really cause hair loss?
Yes. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and restrict oxygen supply to hair follicles, leading to thinning or hair fall over time.
2. Will hair grow back after controlling diabetes?
In many cases, yes. Once blood sugar levels are stabilized and the scalp receives proper nutrients, hair regrowth often improves.
3. What are the best treatments for diabetes-related hair loss?
A balanced diet, regular exercise, proper blood sugar management, and treatments like PRP therapy or hair transplants can help restore hair density.
4. How can I prevent further hair loss?
Manage stress, maintain a healthy scalp, monitor your glucose levels, and avoid harsh hair care products or tight hairstyles.
5. When should I see a doctor for hair loss?
If you notice sudden or severe hair thinning, or if your hair loss is accompanied by other symptoms of diabetes, consult a specialist immediately.
Is alopecia an autoimmune disorder?
Alopecia is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
Is alopecia areata permanent?
Alopecia areata is not necessarily permanent. Many individuals experience hair regrowth, although the condition can recur over time.
Is alopecia areata treatable?
Yes, alopecia areata is treatable, though there is no guaranteed cure. Various treatments, such as corticosteroids, topical medications, and hair transplant options like FUE, can help manage symptoms and promote hair regrowth.
Is it possible to grow hair on bald patches?
Hair can regrow on bald patches. However, the extent and timeline of regrowth can vary among individuals.
Is alopecia areata genetic?
There is a genetic predisposition to alopecia areata. People with a family history of autoimmune diseases may have a higher likelihood of developing this condition.
Why do I have a bald spot on my head?
A bald spot may result from alopecia areata, stress, hormonal changes, or other health conditions. It’s best to consult a medical expert for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels and following a nutritious diet can significantly reduce hair loss related to diabetes.
Reference links:
https://www.dermatologists.org/alopecia-areata/
https://www.medicinenet.com/alopecia_areata/article.htm
Disclaimer: This page is intended for informational or educational purposes and not for promotional use.
Book a Consultation Today
Latest Videos
-

Rajpal Yadav | Bollywood Actor Hair Transplant Journey at QHT Regrow Clinic Haridwar
Click to Watch
-

FUE Hair Transplant Results | DAYA's FUE Hair Transplant Results
Click to Watch
-

Best Hair Transplant Result 2021 || NW Grade VI A || 3,422 Grafts
Click to Watch
-

Best Hair Transplant Result 2022 | Grade 4
Click to Watch
-

YouTuber Mehtab Saifi Hair Transplant
Click to Watch
-

ACP Pradyuman Hair Transplant - Actor's Hair Transplant
Click to Watch