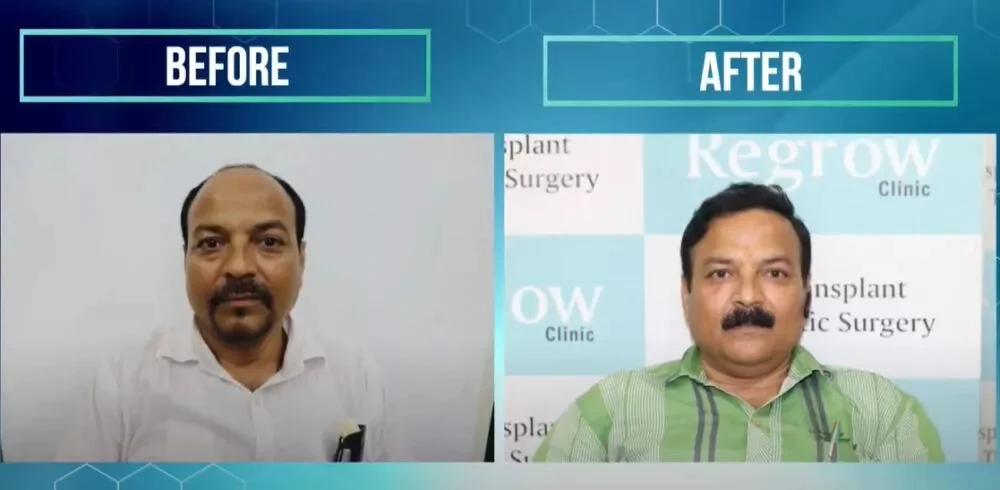
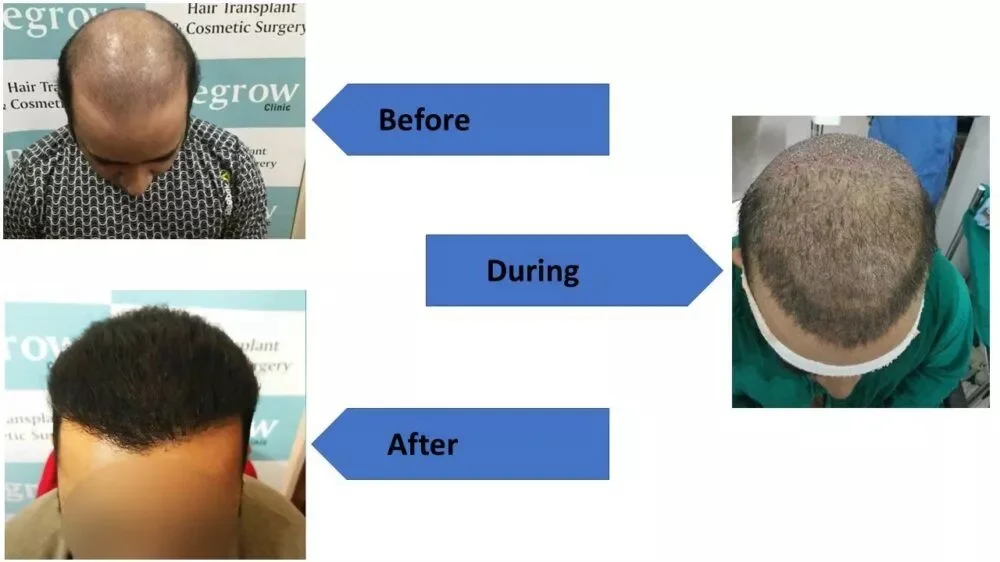
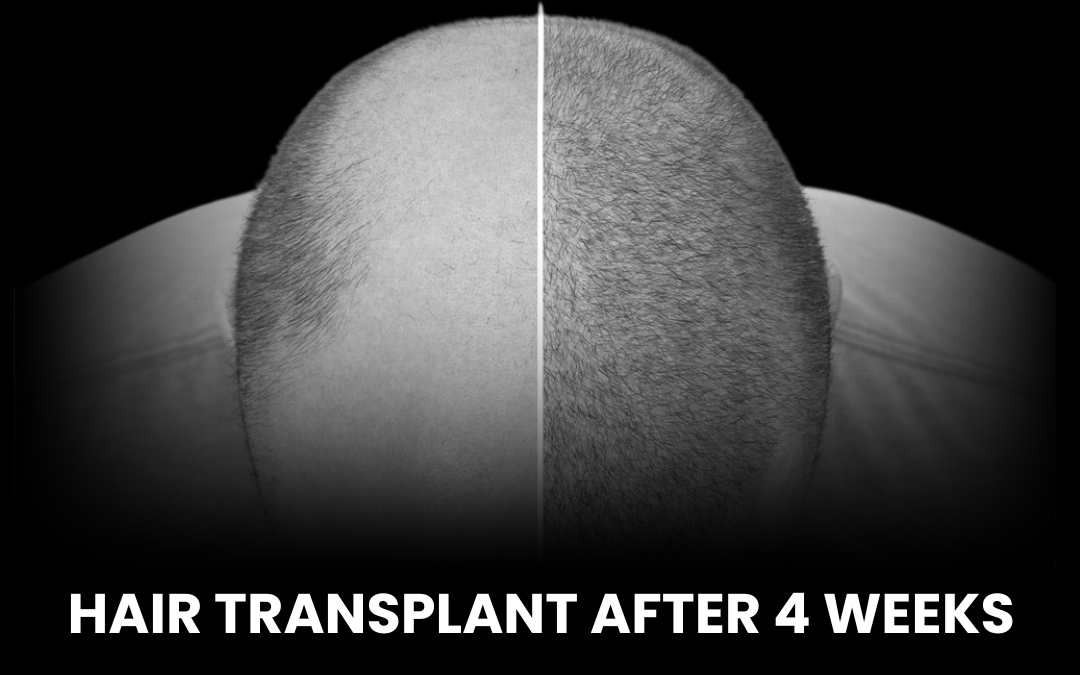
Understanding how genetics affect hair loss and restoration

The good news?
Advances in hair transplant in India and innovative restoration methods offer effective solutions for those struggling with hereditary hair loss. With a team of highly skilled hair transplant surgeons and world-class facilities, QHT Clinic is among the best hair transplant clinics in India. Genetic hair loss, also known as hereditary alopecia, occurs when specific genes passed down through generations influence hair follicle sensitivity and longevity. Unlike temporary hair shedding, this type of hair loss is gradual and progressive.
Family History Matters: If close relatives have experienced baldness or thinning, there’s a high probability that genetics are at play.
Chromosomal Influence: While once believed to be passed primarily from the mother’s side, research suggests that genes from both parents contribute to hair loss patterns.
Hair Follicle Sensitivity: The inherited sensitivity of hair follicles to hormonal changes, particularly Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), is a primary cause of genetic hair loss.
Androgenetic Alopecia, commonly known as male and female pattern baldness, is the leading cause of hereditary hair loss worldwide. It affects over 50 million men and 30 million women in India alone.
Genetic hair loss, also known as hereditary alopecia, occurs when specific genes passed down through generations influence hair follicle sensitivity and longevity. Unlike temporary hair shedding, this type of hair loss is gradual and progressive.
Family History Matters: If close relatives have experienced baldness or thinning, there’s a high probability that genetics are at play.
Chromosomal Influence: While once believed to be passed primarily from the mother’s side, research suggests that genes from both parents contribute to hair loss patterns.
Hair Follicle Sensitivity: The inherited sensitivity of hair follicles to hormonal changes, particularly Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), is a primary cause of genetic hair loss.
Androgenetic Alopecia, commonly known as male and female pattern baldness, is the leading cause of hereditary hair loss worldwide. It affects over 50 million men and 30 million women in India alone.
- Male Pattern Baldness (MPB): Typically starts with a receding hairline and thinning crown, eventually leading to complete baldness.
- Female Pattern Baldness (FPB): More diffused thinning, usually noticeable along the part line, but rarely results in complete baldness.
Other Genetic Hair Loss Conditions
Apart from androgenetic alopecia, some lesser-known hereditary conditions can lead to hair loss: Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune disorder where the body attacks hair follicles, leading to patchy bald spots. Congenital Hypotrichosis: A rare genetic condition causing hair loss from birth or early childhood. Marie Unna Hereditary Hypotrichosis: Leads to progressive hair loss, typically starting in adolescence.Other Genetic Hair Loss Conditions
Apart from androgenetic alopecia, some lesser-known hereditary conditions can lead to hair loss: Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune disorder where the body attacks hair follicles, leading to patchy bald spots. Congenital Hypotrichosis: A rare genetic condition causing hair loss from birth or early childhood. Marie Unna Hereditary Hypotrichosis: Leads to progressive hair loss, typically starting in adolescence. Wondering if it’s too late to act on your genetic hair loss? Consult a hair restoration expert today to find the best approach for preserving your hair. Identifying genetic hair loss involves recognizing patterns and undergoing medical evaluation: Observing Hair Loss Patterns: Is hair thinning following a recognizable pattern? Family History Assessment: A thorough look at immediate and extended family members can provide clues. Genetic Testing: Advanced tests analyze DNA markers to determine predisposition to baldness.Body hair transplant expert says:
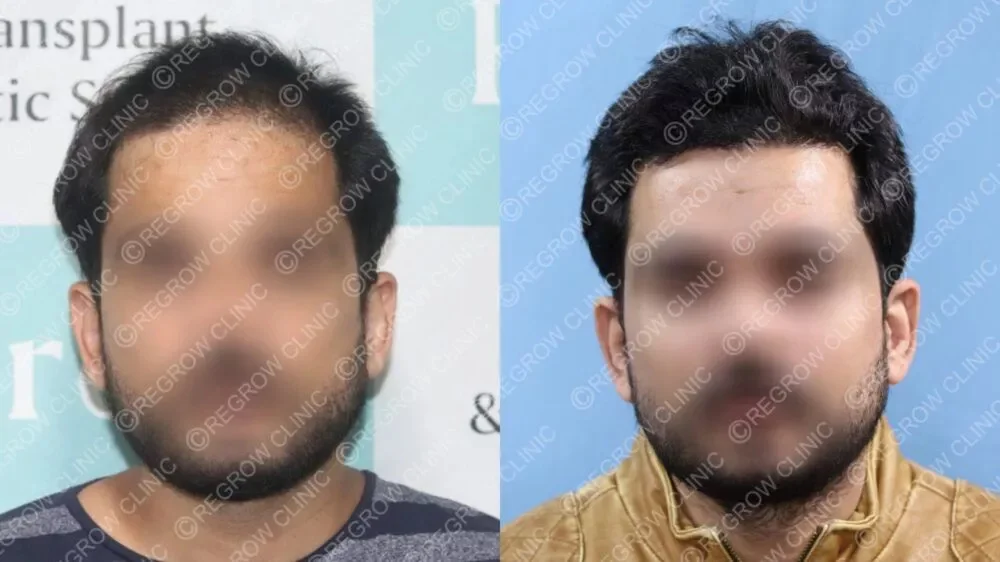
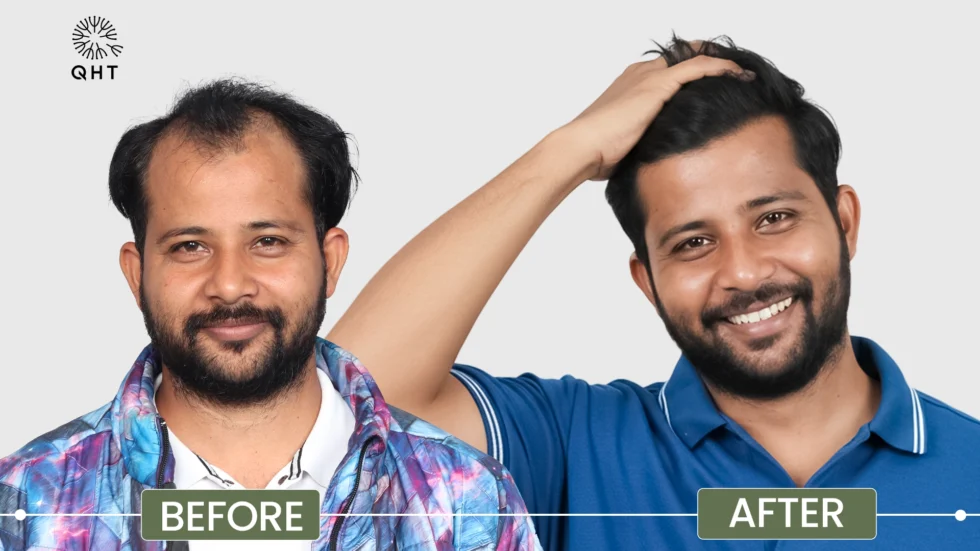
“While genetics cannot be changed, effective treatments can slow or reverse hereditary hair loss. From non-surgical options to advanced restoration techniques, modern dermatology offers promising solutions.”Hair Transplants: A Permanent Solution
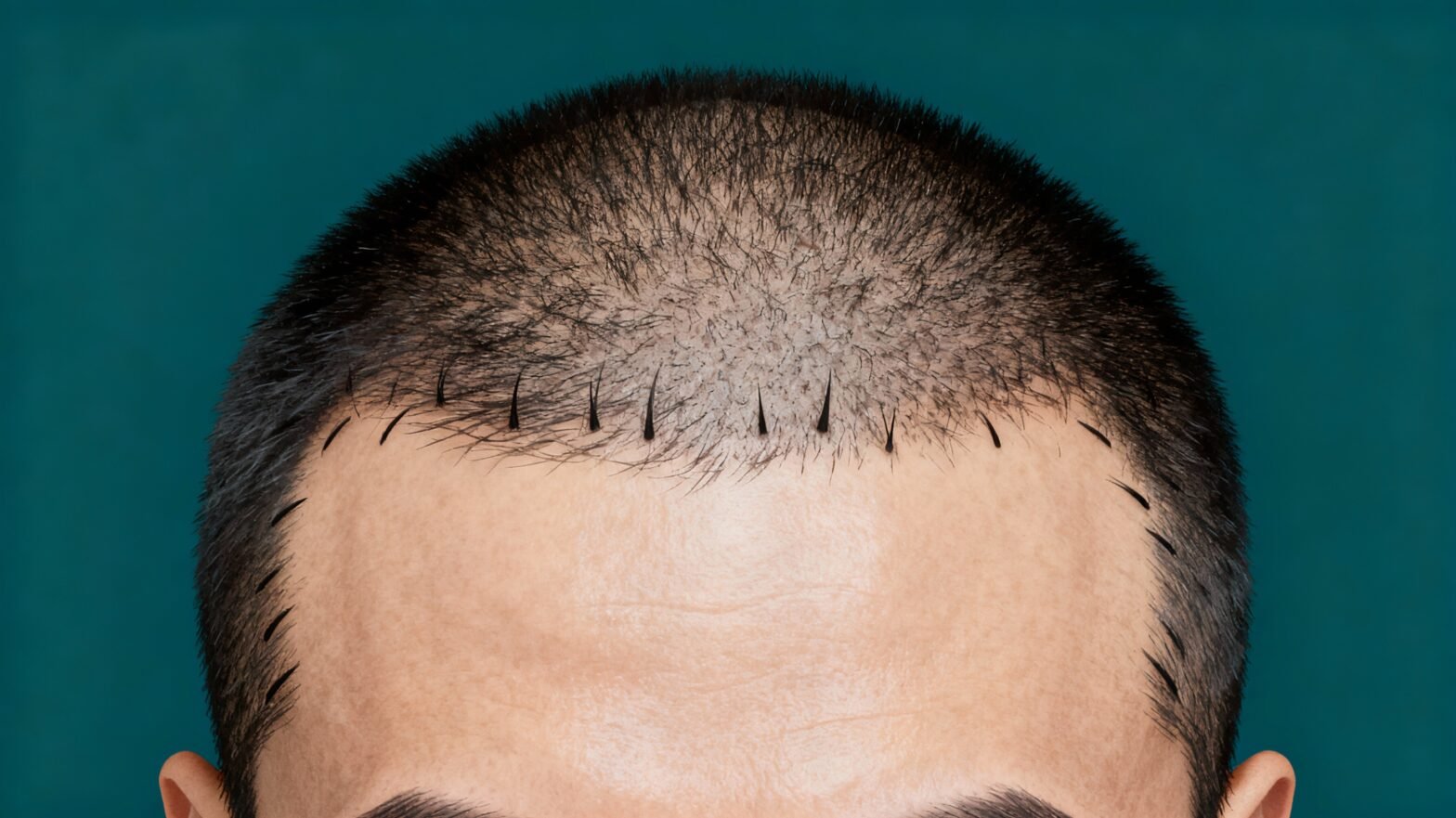
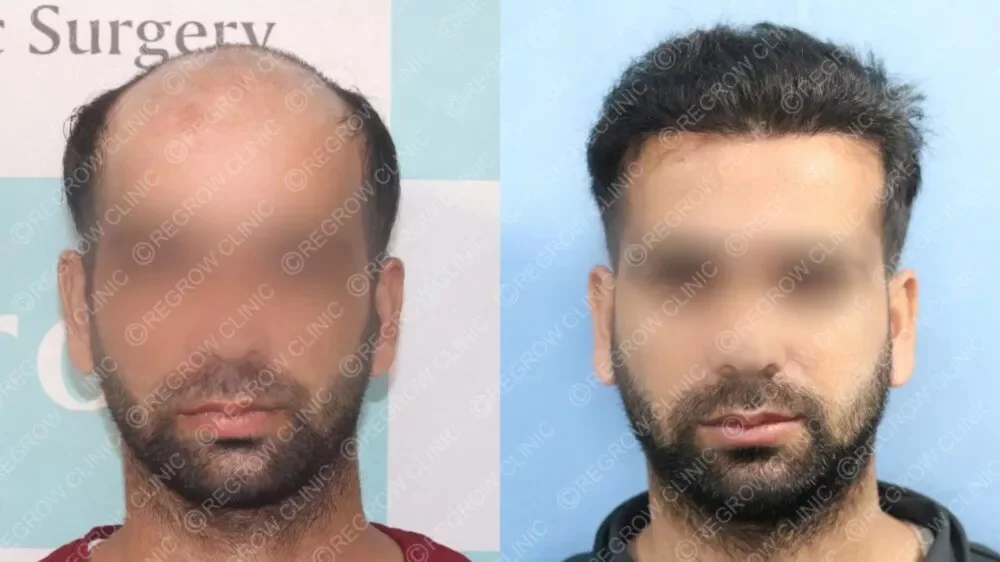
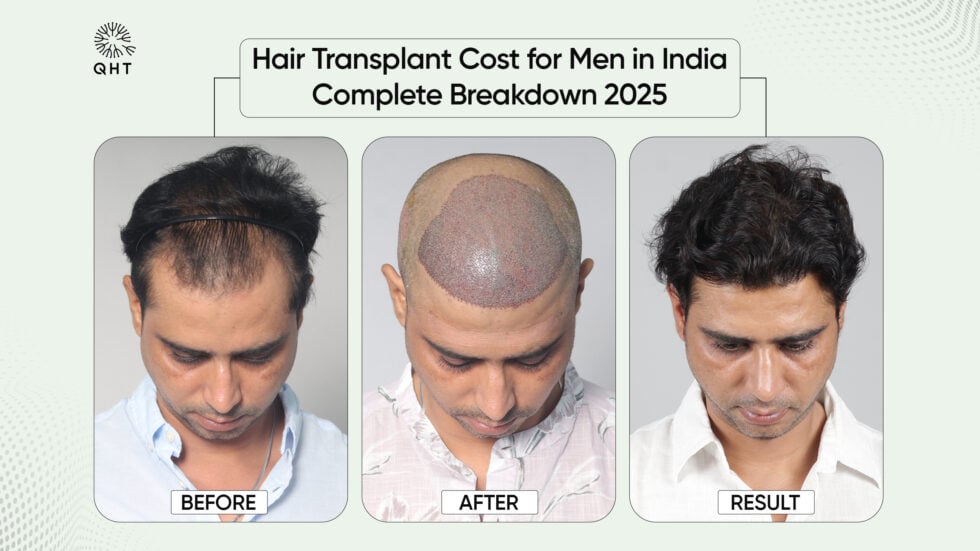
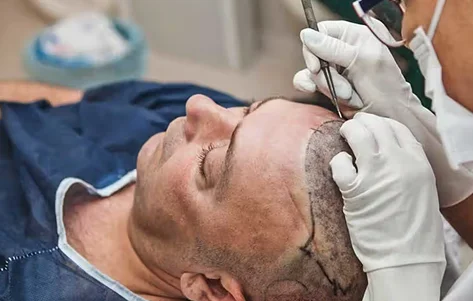
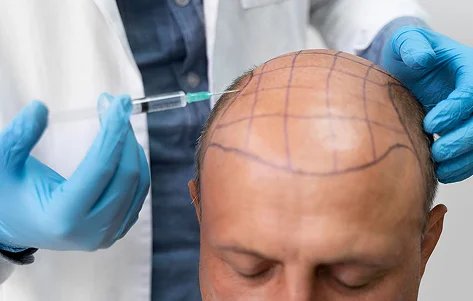
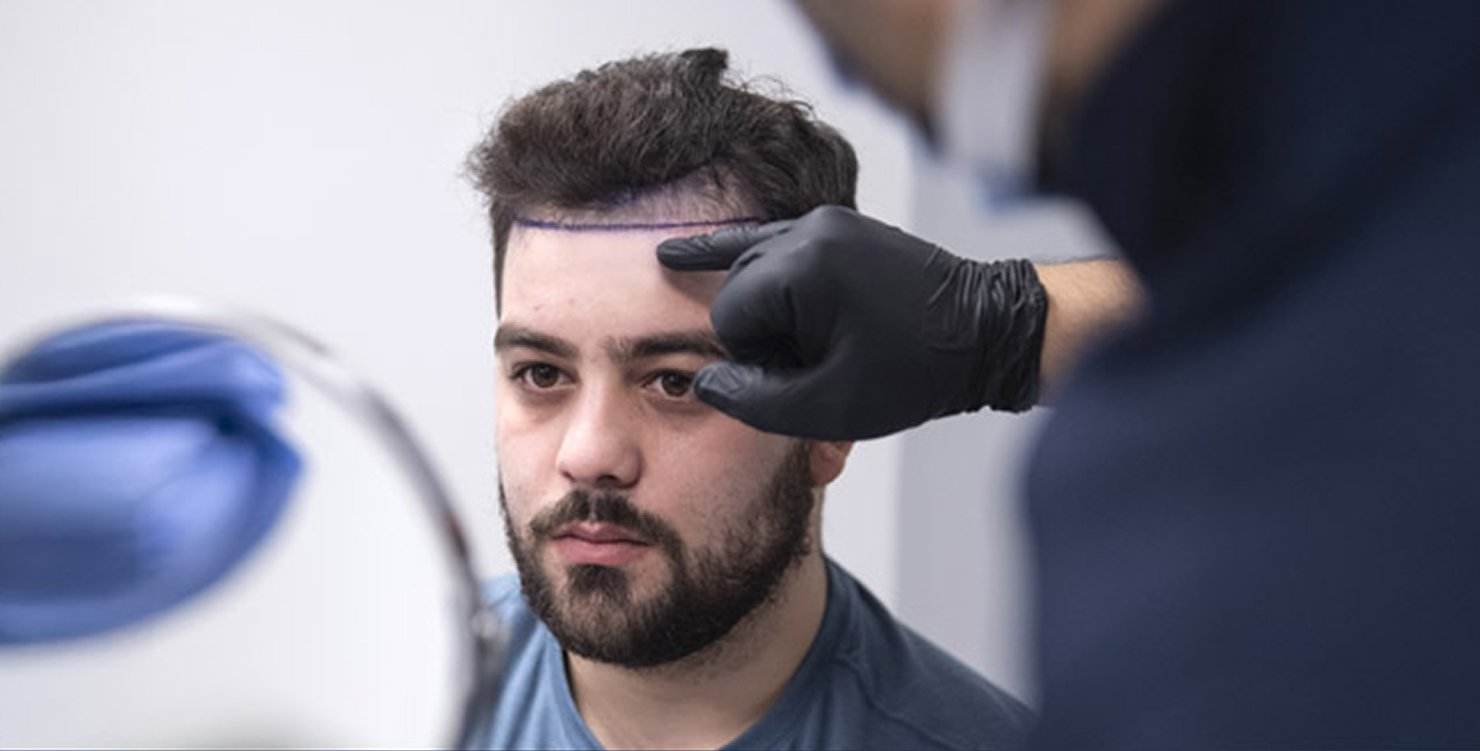
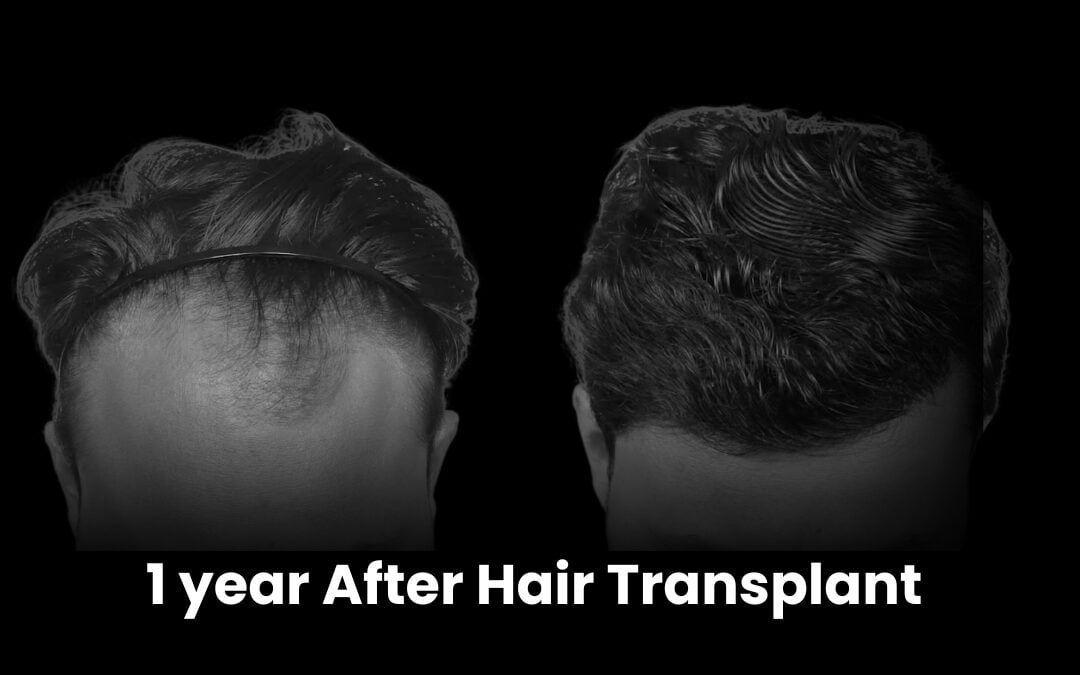
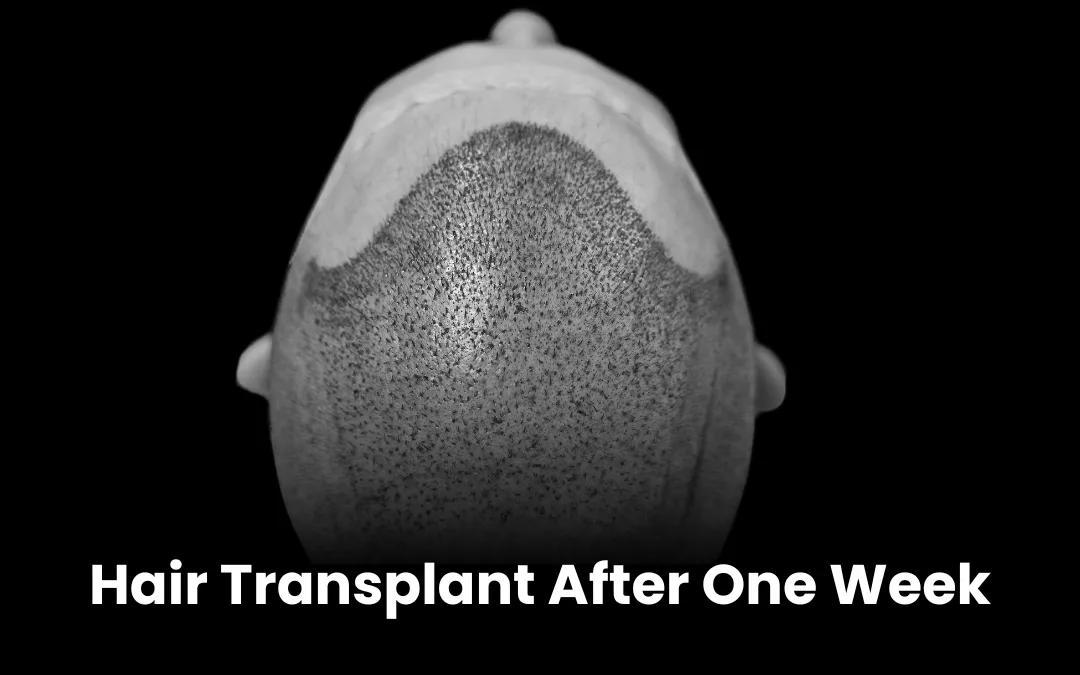
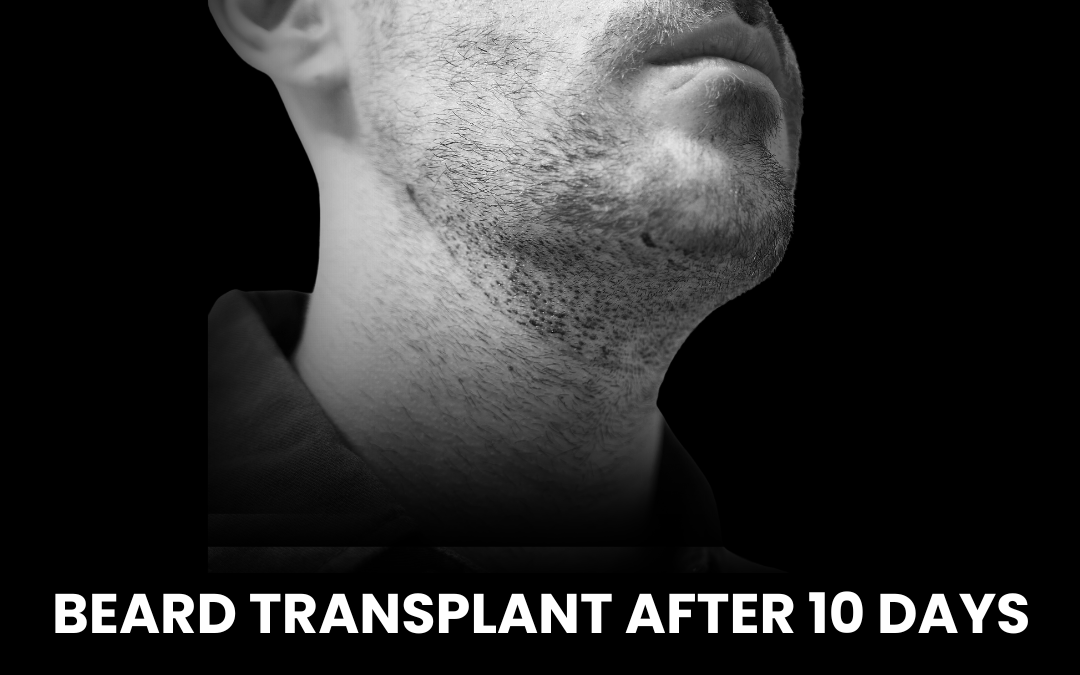
The best hair grafting in India involves advanced FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) and QHT (Quick Hair Transplant) methods. These techniques relocate healthy follicles from donor areas to bald spots, ensuring natural and long-lasting results.Medications and Topical Treatments
- Minoxidil: Stimulates follicles to extend the hair growth phase.
- Finasteride: Blocks DHT, preventing further hair miniaturization.
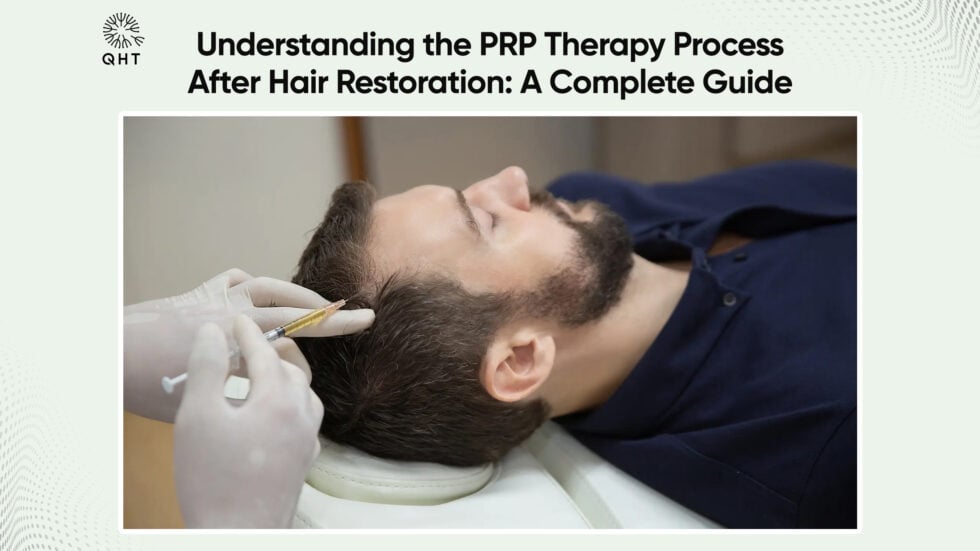
Advanced Therapies: PRP and Stem Cell Treatments
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Uses growth factors to stimulate hair regrowth.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Encourages follicular regeneration, improving hair density.
While genetics play a primary role, external factors can exacerbate hair loss:
Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of essential nutrients like iron, biotin, and protein weakens hair strands, making them brittle and prone to shedding. Without these nutrients, hair follicles struggle to support healthy growth, leading to noticeable thinning over time. Chronic Stress: Prolonged stress raises cortisol levels, which disrupts the natural hair growth cycle and pushes more follicles into the shedding phase. This condition, known as telogen effluvium, can cause significant hair loss, especially during periods of extreme emotional or physical strain. Medical Conditions: Hormonal imbalances from thyroid disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), diabetes, or autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata can weaken hair follicles. These conditions interfere with the hair’s natural renewal process, often causing patchy or widespread thinning.While genetics play a primary role, external factors can exacerbate hair loss:
Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of essential nutrients like iron, biotin, and protein weakens hair strands, making them brittle and prone to shedding. Without these nutrients, hair follicles struggle to support healthy growth, leading to noticeable thinning over time. Chronic Stress: Prolonged stress raises cortisol levels, which disrupts the natural hair growth cycle and pushes more follicles into the shedding phase. This condition, known as telogen effluvium, can cause significant hair loss, especially during periods of extreme emotional or physical strain. Medical Conditions: Hormonal imbalances from thyroid disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), diabetes, or autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata can weaken hair follicles. These conditions interfere with the hair’s natural renewal process, often causing patchy or widespread thinning.While genetics play a primary role, external factors can exacerbate hair loss:
Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of essential nutrients like iron, biotin, and protein weakens hair strands, making them brittle and prone to shedding. Without these nutrients, hair follicles struggle to support healthy growth, leading to noticeable thinning over time. Chronic Stress: Prolonged stress raises cortisol levels, which disrupts the natural hair growth cycle and pushes more follicles into the shedding phase. This condition, known as telogen effluvium, can cause significant hair loss, especially during periods of extreme emotional or physical strain. Medical Conditions: Hormonal imbalances from thyroid disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), diabetes, or autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata can weaken hair follicles. These conditions interfere with the hair’s natural renewal process, often causing patchy or widespread thinning.- Hair Transplants: Best for advanced hair loss cases.
- Medications: Can slow hair thinning and encourage regrowth.
- Non-Surgical Therapies: PRP and laser treatments improve hair density.
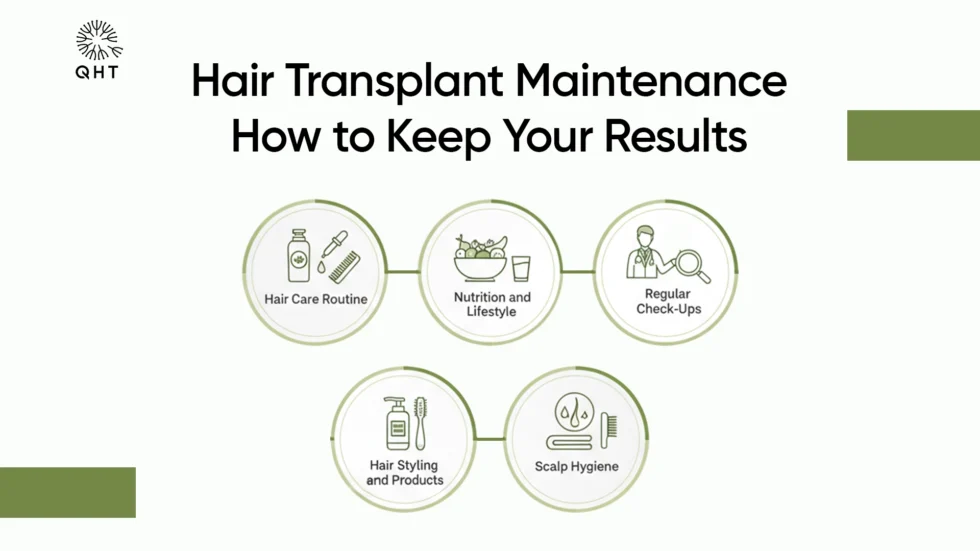
- Lifestyle Adjustments: A nutrient-rich diet, stress management techniques, and proper scalp care help maintain existing hair and support overall hair health.
- Can Your Genes Affect Hair Transplant Success?
- Can Genetic Hair Loss Be Diagnosed Early?
- Is Hair Restoration the Best Option for Genetic Hair Loss?
- At what age does genetic hair loss typically begin?
- How do I know if I need a hair transplant?
Reference Links:
https://www.health.harvard.edu/a_to_z/hereditary-patterned-baldness-a-to-z https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/hair-loss/treatment/transplant Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only and not for promotional use.Book a Consultation Today
Latest Videos
-

Rajpal Yadav | Bollywood Actor Hair Transplant Journey at QHT Regrow Clinic Haridwar
Click to Watch
-

FUE Hair Transplant Results | DAYA's FUE Hair Transplant Results
Click to Watch
-

Best Hair Transplant Result 2021 || NW Grade VI A || 3,422 Grafts
Click to Watch
-

Best Hair Transplant Result 2022 | Grade 4
Click to Watch
-

YouTuber Mehtab Saifi Hair Transplant
Click to Watch
-

ACP Pradyuman Hair Transplant - Actor's Hair Transplant
Click to Watch